The Ultimate Guide to the Industrial LoRaWAN Gateway (R1520LG)
|
|
Time to read 6 min
|
|
Time to read 6 min
The Industrial LoRaWAN Gateway is arguably the most critical component in any modern Industry 4.0 deployment, yet it's often the most misunderstood. What is it, really? It's the powerful, intelligent bridge between your physical machinery and your digital systems.
This definitive guide serves as your single source of truth on the topic. We will break down what defines a true Industrial LoRaWAN Gateway , why edge computing is a non-negotiable for modern IIoT, and what core functions it must perform.
We'll explore essential hardware and software components, compare connectivity options from 4G to LoRaWAN, and demystify industrial protocols. By the end of this guide, you will have a clear framework for selecting, securing, and managing a fleet of gateways at scale.
I've spoken with countless engineers who start their LoRaWAN journey thinking a gateway is just a simple "bridge" to get sensor data to the cloud. They set up a basic packet forwarder, and it works—for a while. But then the real-world challenges hit: What happens if the internet connection drops? How do you manage a fleet of 500 gateways without flying an engineer to each site? How do you connect legacy Modbus equipment without a complex PLC setup?
This is where the conversation shifts from a simple bridge to an intelligent nerve center. A true Industrial LoRaWAN Gateway is no longer a passive device; it's a powerful edge computer designed to solve these problems. It’s the difference between a simple data pipe and a robust, secure, and intelligent platform. This guide will walk you through this evolution, showing how a device like the Robustel R1520LG acts as a "front-line commander" for your entire IoT sensor network.

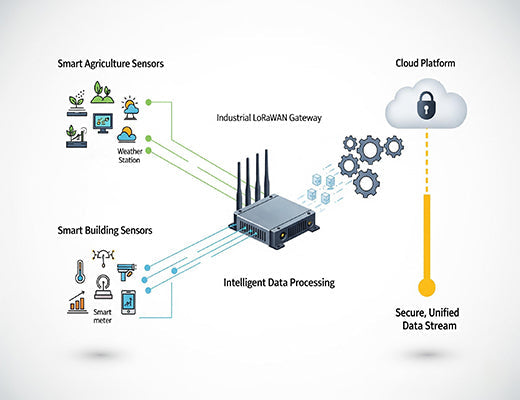
At its heart, an Industrial LoRaWAN Gateway is a ruggedized device that collects data from LoRaWAN sensors and relays it to a network server. But in an industrial context, its capabilities must go far beyond that. It must offer flexibility in how it operates and processes data.
The real 'aha!' moment for many engineers is realizing they can choose an architecture that perfectly fits their needs for security, latency, and reliability. A modern gateway can function as a simple data forwarder for a public network or as a completely self-contained private network server, giving you ultimate control over your data.
Further Reading:
Industrial environments are brutal. Consumer-grade hardware simply won't survive. An Industrial LoRaWAN Gateway must be engineered for reliability from the ground up, with a focus on unbreakable connectivity.
The gateway is your sensor network's only link to the outside world. If that link fails, your entire network is blind. That's why features like a LoRaWAN gateway with cellular backhaul and dual-SIM failover are not luxuries; they are fundamental requirements for any mission-critical deployment. Furthermore, flexible power options like PoE and industrial interfaces for legacy systems are what separate a true industrial product from a prosumer gadget.
Further Reading:

A gateway's true power lies in its software. A closed, proprietary OS limits you to the vendor's roadmap. An open platform, however, unleashes your team's creativity. The R1520LG runs on RobustOS Pro , a hardened operating system based on Debian 11. This isn't just a technical detail; it's a strategic advantage.
A Debian based LoRaWAN Gateway provides a familiar environment for developers, granting access to thousands of open-source packages and the freedom to develop in any language. With support for Docker , you can package any application—from a custom analytics script to a protocol converter—and deploy it seamlessly. This transforms the gateway from a simple network device into a true LoRaWAN edge gateway.
Further Reading:
Managing one gateway is easy. Managing hundreds is an operational nightmare without the right tools. A centralized cloud management platform like Robustel's RCMS is essential for any scalable deployment. It allows for zero-touch provisioning, fleet-wide monitoring, and, crucially, secure remote access and updates.
The ability to securely push an OTA update to a gateway in a remote field or connect it to a major cloud platform like AWS IoT Core without a site visit is what makes a large-scale LoRaWAN network economically viable. This is where the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) of a project is truly won or lost.
Further Reading:
A versatile Industrial LoRaWAN Gateway like the R1520LG is being deployed to solve challenges across numerous verticals, from smart buildings to precision agriculture. Its ability to not only handle LoRaWAN traffic but also integrate with legacy systems via protocols like Modbus makes it a powerful tool for modernization.
These real-world examples show how the technology moves from theory to tangible ROI, whether it's optimizing energy use in a commercial building or boosting crop yields on a farm.
Explore Use Cases:

In the complex world of the IIoT, the debate is no longer about just getting connected. It's about getting connected reliably, securely, and intelligently. An Industrial LoRaWAN Gateway has evolved from a simple data forwarder into a powerful LoRaWAN edge gateway —a true edge computing platform.
By choosing a device like the Robustel R1520LG , you are investing in a complete ecosystem. You get the flexibility of an open, Debian-based OS, the reliability of industrial-grade hardware with resilient connectivity, and the scalability of a powerful cloud management platform. This combination allows you to move beyond a simple proof-of-concept and build a professional, secure, and manageable industrial IoT solution that is ready for the future.
A1: The main difference is control and reliability. Using the built-in ChirpStack LNS creates a private, self-contained network that can operate even if the internet connection fails. Packet Forwarder mode relies on an external server, so if the internet backhaul drops, the gateway stops collecting data.
A2: No. For standard gateway operations, all configurations for networking, LoRaWAN, and failover can be done through an intuitive web-based GUI. The open Debian environment is available for advanced users and developers who want to deploy custom applications with tools like Docker or Python.
A3: Yes, absolutely. The gateway's RS232/RS485 serial ports and its support for protocols like Modbus allow it to act as a data concentrator for both wireless LoRaWAN sensors and wired industrial devices, bridging legacy and modern systems.