The Importance of a LoRaWAN Gateway with Cellular Backhaul
|
|
Time to read 4 min
|
|
Time to read 4 min
You’ve designed a brilliant LoRaWAN solution to monitor assets in a remote field or across a sprawling industrial campus. Your sensors are communicating perfectly with your gateway. But then comes the critical question: how does the gateway itself talk to the internet?
This guide explains the non-negotiable importance of a LoRaWAN Gateway with Cellular Backhaul .
We’ll explore why relying on local Wi-Fi or Ethernet is often a recipe for failure and how features like dual-SIM failover provide the unbreakable connectivity your mission-critical IoT deployment demands.
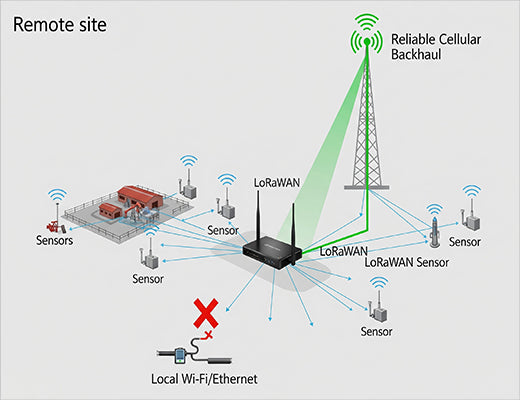
I can't tell you how many times I've seen a meticulously planned IoT project brought to its knees by a single, simple point of failure: the internet connection. A company spends a fortune on sensors and a powerful gateway, only to connect it to a customer's guest Wi-Fi network or a single, vulnerable Ethernet cable. One accidental disconnection, one Wi-Fi password change, and their entire multi-thousand-dollar sensor network goes dark.
This is why the gateway's internet connection, known as its "backhaul," is the most critical link in your entire data chain. For any serious industrial or remote deployment, relying on someone else's infrastructure is a massive risk. A LoRaWAN Gateway with Cellular Backhaul is the professional solution. It gives you a dedicated, reliable, and secure data pipe that you control.

For many industrial IoT applications, cellular isn't just an option; it's the only viable choice. It provides a level of flexibility and reliability that wired or Wi-Fi connections simply cannot match in dynamic, real-world environments.
Even a single cellular connection can be a point of failure. What if your chosen carrier has a local tower outage? This is where a dual-SIM LoRaWAN gateway becomes the gold standard for reliability.
A gateway like the Robustel R1520LG is equipped with two SIM card slots. Here’s how it creates unbreakable connectivity:
This dual-carrier redundancy ensures that a single network outage doesn't take your entire sensor network offline. It's the ultimate insurance policy for your data.

Your LoRaWAN gateway is the heart of your sensor network. Its connection to the internet is the artery that carries all your valuable data. Leaving that critical link to chance by relying on unstable or insecure local networks is a risk not worth taking. A LoRaWAN Gateway with Cellular Backhaul , especially one equipped with dual-SIM failover, provides the dedicated, robust, and reliable connectivity that mission-critical industrial applications demand. It’s a foundational investment in the uptime and success of your entire IoT project.

A1: Not necessarily. LoRaWAN is a very data-efficient protocol. The amount of data sent by hundreds of sensors is often quite small, meaning you can use affordable IoT-specific data plans. The cost of the data plan is almost always far less than the cost of a single instance of downtime.
A2: No. When using a cloud management platform like Robustel's RCMS, the gateway makes a secure outbound connection to the cloud. This means you can remotely access and manage your gateway even if it has a private, dynamic IP address from the cellular carrier.
A3: Yes. A high-quality industrial gateway can be configured to use a wired Ethernet connection as its primary backhaul and automatically failover to its cellular connection if the wired line is cut. This provides an excellent multi-layered resilience strategy.