Modernize, Don't Replace: A Practical Guide to LoRaWAN Modbus Integration
|
|
Time to read 4 min
|
|
Time to read 4 min
Your factory floor is filled with valuable, reliable equipment that speaks the industry's lingua franca: Modbus. The problem? It's tethered by cables.
This guide provides a practical solution to this common challenge: LoRaWAN Modbus integration .
We'll explain how a modern Modbus to LoRaWAN gateway can act as a powerful bridge, untethering your legacy sensors and controllers and bringing their valuable data into your central monitoring system wirelessly. It's the ultimate strategy for modernizing your operations without a costly rip-and-replace overhaul.
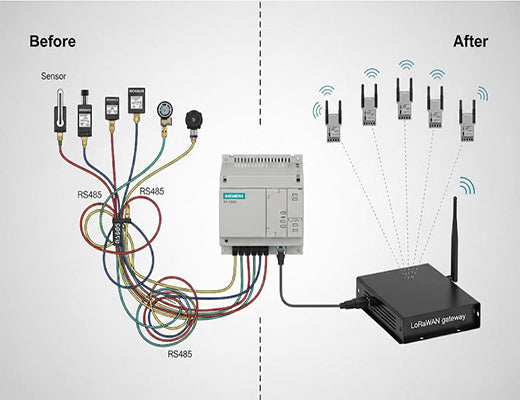
I've walked through countless industrial facilities, and the story is always the same. There are hundreds of perfectly good sensors, VFDs, and power meters, all dutifully communicating over Modbus RTU via long, daisy-chained RS485 cables. This system is the backbone of their operations. But it's also a cage. What happens when you want to monitor a tank that's 500 meters away, across a yard where you can't trench a new cable?
This is where many modernization projects get stuck. The cost and complexity of running new wires are prohibitive. But what if you could make your Modbus devices speak wireless? What if you could bridge that 500-meter gap with a reliable, long-range radio link? This is exactly what LoRaWAN Modbus integration allows you to do. It's about cutting the cord on your legacy systems and giving them a new lease on life.

This is the most common pattern for new or expanded sensor deployments.
This pattern is perfect for connecting entire remote Modbus networks.
This level of sophisticated protocol translation requires more than a basic gateway. You need a true LoRaWAN edge gateway for effective LoRaWAN Modbus integration .
The Robustel R1520LG is the ideal platform for this task. Its key features include:

Your legacy Modbus infrastructure is a valuable asset, rich with data that can drive efficiency and improve operations. You don't need to replace it to modernize. By leveraging a smart LoRaWAN Modbus integration strategy, you can break free from the physical constraints of cables. A powerful Modbus to LoRaWAN gateway acts as the perfect bridge, giving you the freedom to deploy sensors wherever you need them and connect remote assets with ease, unlocking the full potential of your industrial data.

A1: Modbus RTU is the original version of the protocol that runs over serial communication lines (like RS485). Modbus TCP is a newer version that encapsulates Modbus messages within a standard TCP/IP packet, allowing it to run over Ethernet networks. A key role of a gateway is often to translate between these two.
A2: The LoRaWAN portion of the network can support thousands of wireless sensor nodes. When the gateway acts as a Modbus TCP server, it can typically handle hundreds of simultaneous connections from PLCs or SCADA systems, making the architecture highly scalable.
A3: Yes. The LoRaWAN protocol has mandatory end-to-end AES-128 encryption for all wireless data transmissions, ensuring that your industrial data is protected from eavesdropping.