Enhancing Grid Monitoring and AMR with LoRaWAN for Smart Utilities
|
|
Time to read 4 min
|
|
Time to read 4 min
Utility providers for water, gas, and electricity are facing immense pressure to modernize their aging infrastructure, reduce operational costs, and improve service reliability.
This guide explores how LoRaWAN for smart utilities provides a powerful, cost-effective solution to these challenges.
We'll dive into key applications, from next-generation Automated Meter Reading ( LoRaWAN AMR ) to real-time smart grid monitoring , and explain how this long-range, low-power technology is enabling a more intelligent and efficient utility network.
I've talked with operations managers at municipal water and power utilities, and they all describe a similar, daunting reality. Their assets—meters, transformers, pipelines, and substations—are spread across hundreds of square miles, often in hard-to-reach locations. The traditional method of managing this network involves sending technicians out in trucks to manually read meters or inspect equipment. It's slow, expensive, and incredibly inefficient.
This is the core problem that smart utility technology aims to solve. But traditional connectivity options like cellular can be too expensive and power-hungry for a city-wide deployment of tens of thousands of meters. This is where LoRaWAN has emerged as a game-changer. It provides the perfect blend of long-range coverage, low power consumption, and low cost needed to make LoRaWAN for smart utilities a reality.

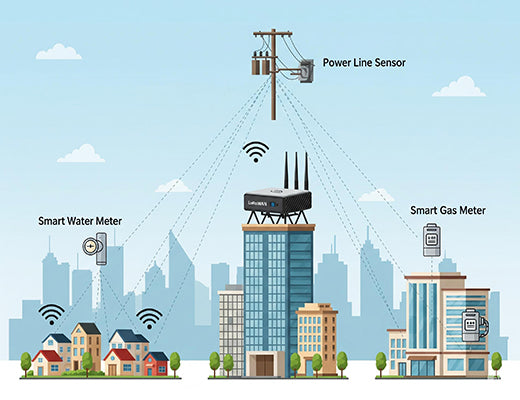
While AMR is a powerful starting point, the same LoRaWAN network can be used for much broader smart grid monitoring .
Utilities can deploy a variety of LoRaWAN sensors connected to a gateway like the Robustel R1520LG to:

LoRaWAN for smart utilities is a transformative technology. It provides a secure, scalable, and cost-effective communication backbone that moves utility providers from a reactive, manual operational model to a proactive, data-driven one. From the massive cost savings of LoRaWAN AMR to the enhanced reliability of real-time smart grid monitoring , LoRaWAN empowers utilities to reduce waste, improve service, and build a more sustainable infrastructure for the future.

A1: Yes. This is one of LoRaWAN's key strengths. Its use of sub-gigahertz frequencies gives it excellent signal penetration capabilities, allowing it to reliably reach meters located in challenging indoor or underground locations where other wireless technologies would fail.
A2: Yes. LoRaWAN has multiple layers of security built-in, including end-to-end AES-128 encryption for all data transmissions. By deploying a private network with a gateway that runs its own network server, the utility maintains complete control and ownership of its data, further enhancing security.
A3: AMR (Automated Meter Reading) is typically a one-way system for collecting consumption data. AMI (Advanced Metering Infrastructure) is a more advanced, two-way system that not only collects data but also allows the utility to send commands back to the meter, for functions like remote disconnect/reconnect. LoRaWAN supports both AMR and AMI applications.