Building a Private LoRaWAN Network: Key Advantages for Security and Reliability
|
|
Time to read 4 min
|
|
Time to read 4 min
When deploying a LoRaWAN solution, you have a fundamental choice: use a public, shared network or build your own.
This guide dives deep into the powerful advantages of building a private LoRaWAN network . We'll explore how taking control of your own infrastructure provides unmatched benefits in security, reliability, data sovereignty, and long-term cost.
For any serious industrial or enterprise application, creating a private LoRaWAN network is not just an option; it's a strategic necessity.
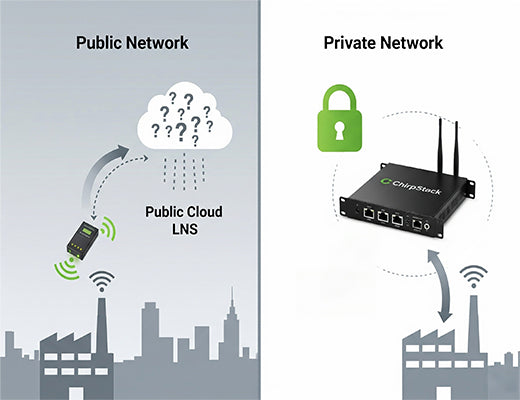
Public LoRaWAN networks, like The Things Network, are a fantastic resource for hobbyists and for getting a quick proof-of-concept running. They've done an incredible job of making the technology accessible. But I've seen the moment of panic in an operations manager's eyes when they realize their factory's critical production data is being routed through a community-run, best-effort network.
For an industrial application, "best-effort" isn't good enough. You need guarantees. You need control. You need to know that your network will be there when you need it most, and that your sensitive data isn't taking a detour through servers you don't manage. This is why the conversation for any commercial deployment inevitably turns to building a private LoRaWAN network . It’s about moving from a shared public utility to your own dedicated, high-performance infrastructure.

The defining feature of a private LoRaWAN network is that you own and control the LoRaWAN Network Server (LNS). Instead of your gateways forwarding packets to a third-party cloud, they forward them to an LNS that you manage.
The most powerful and efficient way to do this is to use a ChirpStack gateway —a LoRaWAN edge gateway that runs the entire LNS software locally. This creates a completely self-contained private LoRaWAN network .
Let's break down why this architectural choice is so powerful for industrial applications. A private LoRaWAN network offers benefits that public networks simply cannot match.
This is the number one reason enterprises choose to build a LoRaWAN network .
What happens to a public network if its cloud servers go down? Your network goes down with it. A private LoRaWAN network is inherently more resilient.
While there's an upfront hardware investment, a private network is almost always more cost-effective at scale.

For hobbyists and small-scale experiments, public networks are an excellent starting point. But for any serious industrial or enterprise application where security, reliability, and data control are critical, the choice is clear. Building a private LoRaWAN network is the professional standard. By investing in a capable ChirpStack gateway , you are not just buying a piece of hardware; you are taking ownership of your entire IoT infrastructure, creating a robust and future-proof foundation for your digital transformation.

A1: Not anymore. Modern all-in-one gateways with pre-installed or easily deployable ChirpStack software have dramatically simplified the process. The basic setup can often be done through a user-friendly web interface, without deep command-line expertise.
A2: At a minimum, you need two things: your LoRaWAN-enabled sensors and a LoRaWAN gateway capable of running a built-in LNS.
A3: Yes. A single industrial-grade gateway can cover an entire factory campus or a large farm. For even larger areas, like a city or a large utility district, you can deploy multiple gateways that all connect to a central LNS that you host, giving you wide-area coverage under your complete control.