LoRaWAN Edge Gateway vs. Basic Packet Forwarder: What's the Real Difference?
|
|
Time to read 4 min
|
|
Time to read 4 min
In the world of LoRaWAN, not all gateways are created equal. You'll often see two terms: a basic packet forwarder and a LoRaWAN Edge Gateway . While they might look similar, the difference in their capability is immense.
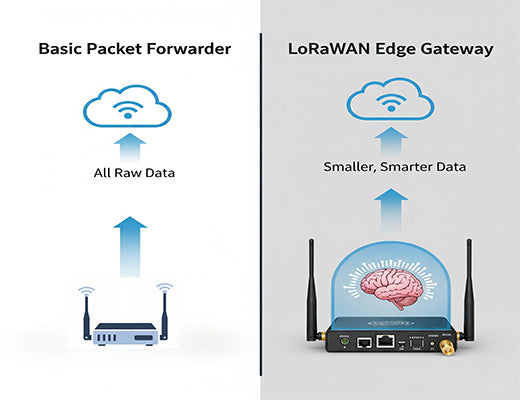
A packet forwarder is a simple radio bridge; a LoRaWAN Edge Gateway is an intelligent on-site computer.
This guide will break down the real LoRaWAN gateway difference , explaining why the edge computing power of a smart gateway is a game-changer for industrial IoT reliability, security, and efficiency.
I've seen many IoT projects get started with the cheapest LoRaWAN gateway they can find. It works, and they're thrilled. The device is a simple packet forwarder —its only job is to hear a LoRaWAN message and blindly forward it to the cloud. But then the problems start. The internet connection at their remote site drops, and they lose hours of critical data. They decide they want to filter sensor readings locally, but their "dumb" gateway has no processing power.
They've learned a hard lesson: they bought a bridge when what they really needed was an intelligent hub. The debate between a LoRaWAN Edge Gateway and a basic packet forwarder isn't about incremental features; it's a fundamental difference in architecture and capability. It's the difference between a simple messenger and an on-site manager who can think for themselves.

A traditional LoRaWAN gateway running in packet forwarder mode is the simplest form of the device.
What it does:
That's it. It has no understanding of the data it's handling. It's a radio-to-IP converter.
Strengths:
Fatal Weaknesses for Industrial IoT:
A LoRaWAN Edge Gateway is a far more powerful and versatile device. It's a ruggedized computer with a LoRaWAN radio. This is the key LoRaWAN gateway difference .
A device like the Robustel R1520LG exemplifies this new class of smart LoRaWAN gateway .
What it does:
Game-Changing Advantages:

The real LoRaWAN gateway difference is intelligence. A basic packet forwarder offers simple connectivity, which might be enough for a non-critical hobby project. But for any serious industrial or commercial application where reliability, security, and real-time response matter, a LoRaWAN Edge Gateway is the only professional choice. It transforms your gateway from a simple liability that goes down with the internet into a powerful, resilient asset that adds true computing value at the edge of your network.

A1: Yes, the upfront hardware cost is typically higher because it has a more powerful processor, more memory, and more advanced software. However, its ability to reduce cellular data costs and, more importantly, prevent costly downtime often results in a much lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
A2: Yes. A flexible edge gateway can be configured to run in either mode. This allows you to start with a simple packet forwarder setup and then later transition to a more powerful private network with a built-in LNS, all on the same hardware.
A3: It's the practice of processing data on the gateway itself, rather than in the cloud. This could be as simple as converting a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, or as complex as running an AI model to detect anomalies in sensor readings.