Optimizing Yields: A Look at LoRaWAN for Smart Agriculture Solutions
|
|
Time to read 4 min
|
|
Time to read 4 min
Modern farming is a high-tech science, but it faces a fundamental challenge: connectivity. How do you collect data from sensors spread across thousands of acres where there's no Wi-Fi and power is scarce? This is where LoRaWAN for smart agriculture comes in.
This guide explores how this long-range, low-power technology is revolutionizing farming.
We'll look at key applications, from precision agriculture with soil moisture sensors to livestock tracking, and explain why a LoRaWAN gateway with cellular backhaul is the essential hub for any smart farming IoT solution.
I've spent a lot of time talking to farmers, and they are some of the most innovative people I know. They're eager to adopt technology to increase yields and reduce costs, but they always hit the same roadblock: the farm itself. It's vast, it's remote, and it's a connectivity desert. You can't run Ethernet cables to the middle of a cornfield, and Wi-Fi won't reach the far pasture.
This is where many smart farming IoT projects fail before they even begin. But what if you could deploy battery-powered sensors that last for years and can send data from miles away? This is the promise of LoRaWAN. It’s a technology that was practically tailor-made for the challenges of the farm. This guide will show you how LoRaWAN for smart agriculture is making data-driven farming a reality.

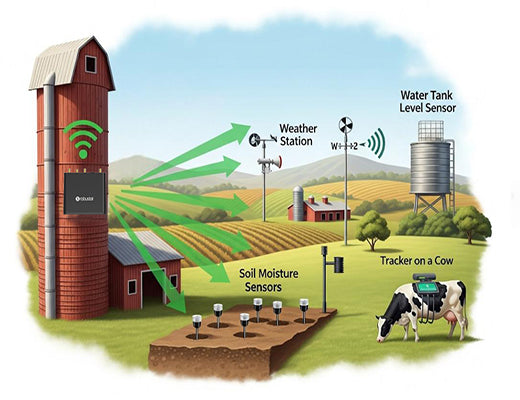
Let's look at how this technology is being used to solve real-world farming problems. The versatility of LoRaWAN for smart agriculture allows for a wide range of applications that drive efficiency and productivity.
This is the killer app for LoRaWAN on crop farms. Instead of watering on a fixed schedule, farmers can make smarter, data-driven decisions.
For ranches and dairy farms, knowing the location and health of your animals is critical.
All this data is useless if you can't access it. On a remote farm, the only reliable internet backhaul is cellular.
A LoRaWAN gateway with cellular backhaul , like the Robustel R1520LG , is the essential hub of the smart farm. It performs two critical roles:

LoRaWAN for smart agriculture is no longer a futuristic concept; it's a practical, proven technology that is delivering real ROI to farmers today. By providing a cost-effective way to connect thousands of sensors over vast, remote areas, it unlocks the data needed for true precision agriculture . From saving water to protecting livestock, this smart farming IoT solution empowers farmers to work smarter, reduce waste, and ultimately, increase the world's food supply.

A1: A single industrial-grade LoRaWAN gateway can typically support thousands of sensors. The exact number depends on how frequently each sensor transmits data and the data rate used, but for typical smart agriculture applications, the capacity is massive.
A2: No. LoRaWAN operates in the unlicensed ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) radio bands (e.g., 915 MHz in North America, 868 MHz in Europe). This means you can set up your own private network without any licensing fees.
A3: Yes. LoRaWAN supports bidirectional communication. You can send a "downlink" command from the gateway back to a LoRaWAN-enabled controller to turn a pump on or off, open a gate, or perform other control actions.