A Guide to VPNs on Industrial Routers for Secure Remote Access
|
|
Time to read 5 min
|
|
Time to read 5 min
VPNs on Industrial Routers are the cornerstone of modern OT cybersecurity, creating a secure, encrypted "tunnel" over the public internet to your remote equipment. This guide explains what a VPN is, why it's non-negotiable for secure remote access to devices like PLCs, and breaks down the most common protocols like IPsec and OpenVPN.
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is the most critical technology for securing data and remote access for any industrial device connected to the internet.
Industrial routers must support a comprehensive suite of VPN protocols (IPsec, OpenVPN, WireGuard, etc.) to ensure compatibility with corporate IT policies.
Using a cloud platform like RCMS can dramatically simplify the deployment of complex VPNs, eliminating the need for static public IP addresses on SIM cards.
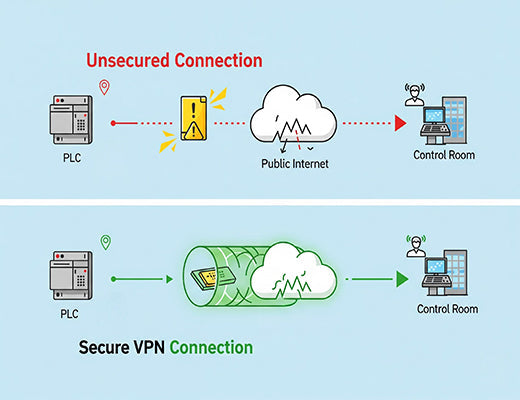
I'll never forget a conversation with a frantic operations manager. His team had connected a remote water pump station to the internet for monitoring, but they'd used a simple port forward to get access to the PLC. A week later, their system was crippled by a ransomware attack. They left the digital front door wide open, and someone walked right in.
Let's be clear: in the industrial world, connecting a device to the internet without a VPN is an act of extreme negligence. It's not a matter of if you'll be attacked, but when.
The good news? The solution is built right into any professional Industrial Cellular Router. That solution is a VPN. This guide will demystify what a VPN does and why it's your first and most important line of defense.

A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, creates a secure and private connection over a public network (the internet). Think of it like this: the internet is a busy public highway. Sending data without a VPN is like sending a postcard—anyone who intercepts it can read it. Using a VPN is like putting that postcard inside a locked, armored truck. The data is placed inside an encrypted tunnel, making it completely unreadable to anyone without the key.
For industrial applications, this is critical for two reasons:

Let's be honest: setting up VPNs, especially for a large fleet of devices, can be complex. You have to deal with certificates, static IP addresses, and complex firewall rules. This is where a cloud management platform like RCMS becomes a game-changer.
The real 'aha!' moment for many of our customers is when they discover a tool like RobustVPN, a feature within RCMS. It completely automates the complex setup of an OpenVPN network.

In the modern IIoT landscape, remote access is essential for efficiency, but unsecured access is a recipe for disaster. VPNs on industrial routers are the non-negotiable technology that allows you to have both. By choosing a router with a comprehensive suite of VPN protocols and a powerful cloud management platform to simplify deployment, you can build a remote operations system that is not only efficient but also fundamentally secure.
Learn More in our main guide:
A1: There is no single "best" protocol; it depends on the use case. IPsec is often considered a gold standard for permanent site-to-site tunnels to corporate offices. OpenVPN is extremely popular and flexible for client access and cloud integration. The most important thing is that your router supports multiple options to fit your IT department's requirements.
A2: Yes, all VPNs add a small amount of overhead due to the encryption process, which can slightly reduce the maximum throughput. However, the processors in modern industrial routers are designed to handle this encryption with minimal performance impact. The security benefits far outweigh the minor speed reduction.
A3: Yes, absolutely. This is one of the most significant advantages of using a cloud-managed VPN solution like Robustel's RCMS with RobustVPN. The router establishes an outbound connection to the cloud VPN server; your client also connects to that server, and the platform bridges the two, completely bypassing the need for a public IP on the device.