How to Secure Your Remote Access Control System: A Cybersecurity Guide
|
|
Time to read 5 min
|
|
Time to read 5 min
This guide explains how to secure your remote access control system by implementing a multi-layered, "defense-in-depth" security strategy. We'll cover the three critical pillars of a secure remote access control architecture: creating an encrypted VPN tunnel to protect data in transit, hardening the on-site gateway to prevent direct attacks, and leveraging a secure cloud platform for management. Following these best practices is essential for protecting your physical premises in the IoT era.
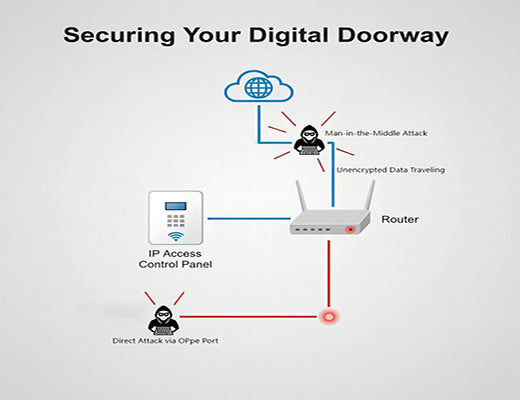
Connecting your access control system to the internet without a robust security strategy is a major risk.
A multi-layered security approach is essential, focusing on the Data, the Device, and the Management Platform.
The most critical component is a VPN (Virtual Private Network), which creates an encrypted "tunnel" for your data over the public internet, making it unreadable to outsiders.
Choosing an industrial router with a hardened operating system, a powerful firewall, and a development process certified to standards like IEC 62443 is a non-negotiable requirement.
I was in a meeting with a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). He told me, "I love the idea of managing all our doors from the cloud. My fear? That someone could hack the router at our front door and unlock it from the other side of the world."
He's right to be concerned. As we connect our physical security infrastructure to the internet, we are also exposing it to new potential threats. A poorly secured connection to your access control iot devices is worse than no connection at all.
Let's be clear: a secure system is not an accident. It is the result of a deliberate, multi-layered design. This guide will walk you through the essential cybersecurity principles for building a system you can truly trust.

This is your first and most important line of defense. All communication between your on-site router and your cloud platform must travel through a secure, encrypted VPN (Virtual Private Network).
Your on-site router is your fortress wall; it must be impenetrable. This is where choosing a professional industrial router over a consumer device is critical.
Your cloud platform is your command center; its security is just as important.

Achieving secure remote access control in an IoT world is about building a system of trust from the ground up. It starts with protecting your data with a VPN, is reinforced by a hardened and certified gateway at the edge, and is completed by a secure platform for management. By choosing a solution provider who treats security as a core design principle, not just a feature, you can confidently embrace the power of cloud management while keeping your physical premises safe and secure.
Further Reading:
A Guide to Access Control IoT Devices: Secure, Scalable, and Remotely ManagedHow to Build a Cloud-Managed Access Control System: A 4-Step GuideCost-Effective Access Control for Multiple Doors: A Guide Using the R1520Choosing the Best Router for Your Access Control System: R2111 vs. R1520
A1: Both are highly secure. IPsec is an industry standard often used for creating a permanent, always-on "site-to-site" tunnel between your remote location and a central server, which is a very common architecture. OpenVPN is often easier and more flexible for providing access to individual remote users or connecting to modern cloud platforms. A professional router should support both.
A2: "Hardening" is the process of securing a system by reducing its "attack surface." This involves removing all unnecessary software, disabling unused services, closing all non-essential network ports, and applying the most secure configuration settings by default.
A3: Don't just rely on marketing materials. Ask for proof. Ask if their development process is certified to a standard like IEC 62443-4-1. Ask if their products undergo regular third-party penetration testing. A vendor who is serious about security will be transparent and proud to share this information.