RobustLink - CLI Access
|
|
Time to read 6 min
|
|
Time to read 6 min
The RCMS CLI access feature, available through RobustLink, is a secure web-based portal that gives administrators direct command-line interface control over their remote Robustel devices.
This powerful tool is designed for network professionals and power users who need to perform rapid diagnostics, granular configuration changes, and scripted actions that go beyond the capabilities of a graphical user interface (GUI).
It’s your direct, unhindered line to the core of your device, accessible from anywhere.
In today's world of intuitive graphical interfaces, it might seem old-fashioned to get excited about a command line. Don't get me wrong, a good GUI is fantastic for visualizing data and managing day-to-day operations. Our entire Robustel Cloud Manager Service (RCMS) platform is built on that principle. But I've been in situations—and I'm sure you have too—where you need to be surgical. You need speed, precision, and the ability to run a command that a button or menu just doesn't offer.
This is where we open our RCMS toolbox and pull out a specialist instrument: the RCMS CLI access tool. If RCMS is the Swiss Army Knife for your IoT deployment, think of this as the high-precision pliers. It’s for the tasks that require a level of control and directness that only a command line can provide. So, let’s get our hands dirty and explore what it can do.
Simply put, RCMS CLI access is a terminal in your web browser. Through the RobustLink feature, it establishes a secure connection directly to your remote Robustel device, dropping you right into its command-line interface. You don't need to set up SSH, worry about firewall rules, or require a public IP address on the remote device. It just works.
So, why should this be part of your workflow?
ping and traceroute directly from the device itself, giving you the most accurate picture of its network environment.
This is where the lightbulb goes on for many admins. Realizing you can perform a live packet trace or force a cellular network rescan on a device hundreds of miles away, all from a browser tab, fundamentally changes your remote management capabilities.
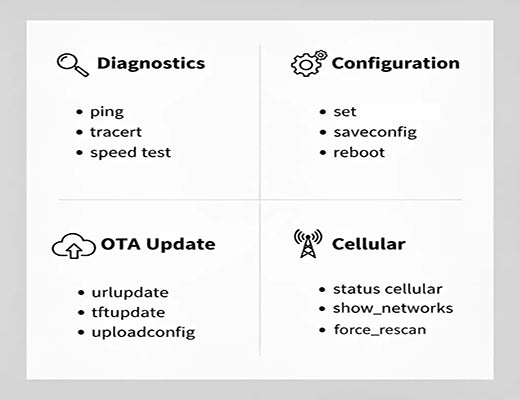
The true power of the RCMS CLI access tool is the comprehensive set of commands at your fingertips. Instead of just dumping a list on you, let’s break them down by what you’re trying to achieve.
This is your first stop for any connectivity issue. These commands let you test network paths and get real-time feedback.
ping: The classic tool to check host reachability and latency.
traceroute: Discover the path your packets are taking to a destination host.
status: Get a high-level overview of running system information.
show: Dive deep into system configurations, including network settings, firewall rules, and more.
speedtest: Run a network speed test directly from the router.
Need to make a change on the fly? These commands provide direct configuration control.
set: The primary command for setting system configuration parameters.
add / del: Add or delete entries from configuration lists (e.g., firewall rules, static routes).
saveConfig: Save your running configuration so it persists after a reboot.
reboot: Perform a cold restart of the device. Essential after certain configuration changes.
do: Manually set the state of a digital output.
Manage your device's software and configuration files remotely.
urlupdate: Update the device firmware from a URL (HTTP or FTP).
tftpupdate: Update firmware or configuration using TFTP.
UploadConfig: Back up the current device configuration to an FTP server.
ipsec_cert_get / ovpn_cert_get: Download certificates for IPsec or OpenVPN setups.
For our cellular routers, these commands offer fine-tuned control over modem behavior—something you rarely find in a GUI.
show_networks: Scan for and display all visible cellular networks.
select: Manually force the modem to connect to a specific network operator.
add_preferred / delete_preferred: Manage the list of preferred PLMNs for smart roaming.
force_rescan: Trigger a new scan for available cellular networks.
Let's make this practical. Imagine a remote point-of-sale kiosk is still online and showing up in RCMS, but the staff is complaining that credit card transactions are extremely slow or timing out. The device is connected, but its performance is crippling the business operations. What do you do?
With RCMS CLI access, your process looks like this:
ping 8.8.8.8. The command doesn't fail, but the results are alarming. The round-trip times are erratic and high: 250ms, 800ms, 450ms. This immediately confirms a severe network latency and stability issue.show cellular to check the modem's real-time signal metrics. The output shows a poor RSRP of -112dBm and a low SINR. This clearly indicates a weak, noisy cellular connection.show_networks to scan for all visible cellular networks. The results confirm your suspicion: the primary carrier's network is visible and available. You note its PLMN ID (e.g., 23410). Now, for an immediate fix, you issue a direct order: select 23410. This command doesn't just suggest a change; it instructs the modem to immediately attempt to register on that specific network.ping 8.8.8.8 again. The difference is night and day. The round-trip times are now stable and low, consistently showing 77ms, 72ms, 75ms.In less than five minutes, you used the precision of the CLI to diagnose a performance issue and execute a surgical network change. This ability to directly command the modem's behavior in real-time is a powerful troubleshooting technique that goes far beyond what's possible with a simple reboot.
It’s natural to be concerned about opening up command-line access to devices. However, the RCMS CLI access is built on a secure foundation. All communication is tunneled through the RCMS platform, meaning the device itself doesn't expose any open ports to the internet. Access is controlled by your RCMS user permissions, providing a secure and auditable trail.
This combination of deep, powerful access and robust, centralized security is what makes RCMS CLI access an indispensable tool for any serious IoT deployment.
A1: It's highly secure. The entire session is encrypted and tunneled through the RCMS platform. You do not need to open any incoming ports on your remote device's firewall or have a public IP address, which significantly reduces its attack surface.
A2: This is a risk with any form of remote management. We recommend having a solid understanding of the commands before executing them. However, since the management tunnel is initiated from the device to RCMS, you can often still access the device via the CLI to revert the change even if its primary WAN connection is misconfigured. You can learn more about best practices in our Remote Device Management guide.
A3: The CLI provides access to the built-in command set of RobustOS for configuration and diagnostics. For installing custom applications, you should use the dedicated App Center within RCMS, which is the proper and supported method for extending device functionality. You can compare features like the RCMS report and CLI in our previous article.


