Remote Troubleshooting for CNC Routers: Diagnosing Problems from Afar
|
|
Time to read 4 min
|
|
Time to read 4 min
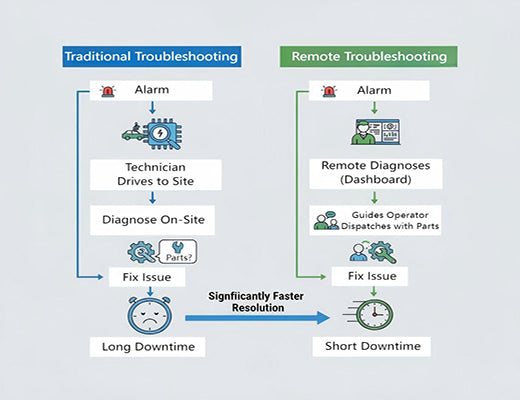
This guide focuses on remote troubleshooting for CNC routers, explaining how leveraging real-time data can transform your maintenance strategy. Instead of immediately dispatching a technician for every issue, connecting your CNC router allows your experts to diagnose many problems remotely by analyzing live status updates, historical alarm codes, and performance data. This approach dramatically speeds up resolution, minimizes costly downtime, and optimizes your field service resources.
Remote troubleshooting uses data from a connected CNC router to diagnose faults without needing an engineer on-site initially.
It shifts the maintenance model from "dispatch first, diagnose later" to "diagnose first, dispatch if necessary."
Key enablers are real-time CNC alarm monitoring, access to historical operational data, and secure remote access to the machine's parameters via an edge gateway.
This approach significantly reduces Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) and slashes the operational cost associated with unnecessary "truck rolls."
The dreaded call comes in: "Machine #5 is down!" Your best technician grabs their toolkit and starts the hour-long drive to the site, completely blind to the actual problem. They arrive, spend another hour diagnosing, only to find it was a simple parameter setting error that could have been fixed remotely in minutes. Millions of dollars are lost globally each year due to this inefficient "dispatch first" maintenance model for assets like your CNC router.
What if your technician could arrive already knowing the likely cause? What if they could fix 80% of the problems without ever leaving the office?
Let's be clear: this isn't a futuristic dream. This is the reality enabled by effective remote troubleshooting for CNC routers.

The traditional approach is wasteful and slow. Remote diagnostics offers a smarter path.
While general remote monitoring gives you status, effective troubleshooting requires specific diagnostic data points, accessed via an edge gateway:
The 'aha!' moment is realizing the edge gateway is your remote "eyes, ears, and hands."

Stop treating every CNC router alarm as a five-alarm fire requiring an immediate, expensive site visit. By implementing a robust remote troubleshooting strategy—leveraging real-time data access and secure remote connectivity enabled by an industrial edge gateway—you can transform your maintenance operations. Diagnose problems faster, reduce costly downtime, and empower your technicians to fix more issues from anywhere, turning your maintenance team from reactive firefighters into proactive problem solvers.

A1: This varies greatly by manufacturer and controller model, but modern controllers often provide very specific alarm codes and sub-codes that can pinpoint the issue to a specific component (e.g., a specific servo drive) or condition (e.g., loss of lubrication pressure). Accessing this exact code remotely is key.
A2: Yes, if done correctly using a professional solution. Access must always be initiated through a secure, encrypted VPN tunnel, ideally managed by a central platform like RCMS that provides authentication and audit logs. Direct exposure of the CNC router or gateway to the public internet is extremely insecure and should never be done.
A3: Remote troubleshooting primarily focuses on diagnosing existing problems faster. However, the data collected for troubleshooting (like historical alarm frequency or increasing motor current trends) is the essential input for a separate predictive maintenance program, which aims to predict failures before they occur. The same connectivity infrastructure enables both.