An Introduction to the Modbus RTU to TCP Gateway Function
|
|
Time to read 5 min
|
|
Time to read 5 min
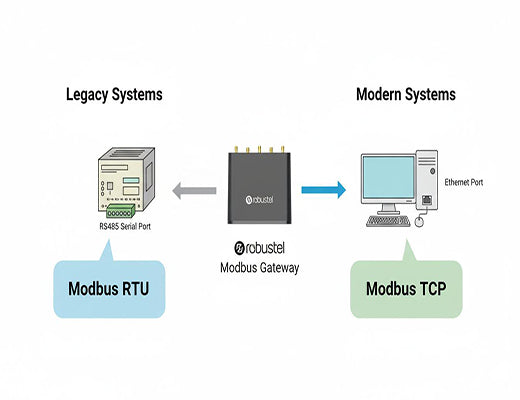
The Modbus RTU to TCP gateway function is a critical piece of technology for modernizing industrial networks. It's a feature built into many industrial routers and gateways that acts as a protocol converter, allowing modern, IP-based SCADA systems (Modbus TCP Masters) to seamlessly communicate with legacy serial devices (Modbus RTU Slaves) like PLCs, VFDs, and power meters.
Modbus is the most common language in industrial automation, but it comes in two main "dialects": Modbus RTU for serial networks and Modbus TCP for modern Ethernet/IP networks.
A Modbus RTU to TCP gateway acts as a "translator" between these two dialects.
This function allows you to preserve your investment in reliable legacy serial devices while integrating them into a modern, centralized monitoring and control system.
Using an industrial router with a built-in Modbus gateway is a cost-effective, all-in-one solution that eliminates the need for separate converter boxes.
In the world of industrial automation, there is one language that has stood the test of time: Modbus. For over 40 years, it has been the reliable, de facto standard for how industrial devices talk to each other. But as networks have evolved from simple serial cables to complex IP networks, Modbus has evolved too.
This has created a common challenge I see in factories all the time: you have a modern SCADA system on your office network that speaks Modbus TCP (over Ethernet), but your most critical and reliable equipment on the factory floor still speaks Modbus RTU (over a serial RS485 connection).
How do you make them talk to each other? Let's be clear: you don't need to rip and replace your trusted serial devices. You just need a good translator. This guide will give you a quick and clear introduction to the essential Modbus RTU to TCP gateway function.

Think of Modbus as a language with two different dialects. The underlying vocabulary (the function codes for reading and writing data) is the same, but the way it's spoken and transmitted is different.
A device that only speaks RTU cannot understand a device that only speaks TCP, and vice versa.
This is where the Modbus RTU to TCP gateway comes in. It's a device (or, more commonly, a software function within an industrial router) that acts as a bilingual translator.
Here's how it works in the most common scenario:
The real 'aha!' moment is realizing that from the SCADA Master's perspective, it looks like it's talking directly to a Modbus TCP device. The entire translation process is completely transparent.


The Modbus RTU to TCP gateway function might sound like a niche technical feature, but it is one of the most powerful and practical tools for any industrial modernization project. It's the invisible translator that allows the past and the present of your factory to communicate seamlessly. When choosing your next industrial router, ensuring it has this robust gateway capability is a critical step in building a flexible, cost-effective, and future-proof network.
Learn More in our main guide:
A1: Yes, absolutely. This is a less common but important scenario where you might have a legacy HMI or device that can only act as a Modbus RTU Master, and you need it to communicate with a modern Modbus TCP slave device. A full-featured gateway can handle this reverse translation as well.
A2: They are different. "Transparent Mode" (or Serial-to-TCP) simply wraps any serial data into an IP packet without understanding what the data is. A Modbus RTU to TCP gateway, on the other hand, actively understands and interprets the Modbus protocol, allowing it to perform intelligent routing and connect multiple masters to multiple slaves. The Modbus gateway function is a more sophisticated and purpose-built solution for Modbus networks.
A3: This depends on the specific device, but on an RS485 network, the standard allows for up to 32 "unit loads." This means you can typically connect up to 32 Modbus RTU slave devices (like PLCs, VFDs, etc.) to a single serial port on your gateway, which can then poll all of them.