Industrial Router vs. IoT Gateway: What's the Real Difference?
|
|
Time to read 6 min
|
|
Time to read 6 min
Choosing between an Industrial Router vs. an IoT Gateway is a critical first step in any IIoT project.
In short: an Industrial Router's primary mission is to provide secure, reliable internet connectivity for your IP-based devices.
An IoT Gateway does that, plus it acts as a smart bridge to connect legacy non-IP devices, translating their data and often processing it locally with edge computing.
I've had this conversation with countless engineers. They're tasked with connecting a factory floor or a remote utility site. They have a modern IP camera that needs a reliable connection, but they also have a 20-year-old PLC with a serial port that holds critical production data. They start searching and immediately run into a wall of confusing terms: Industrial Router, IoT Gateway, Edge Gateway... Aren't they all just boxes that connect things to the internet?
Well, yes and no. And that distinction is the difference between a successful, scalable project and a future full of headaches.
Let's be clear: choosing between an Industrial Router vs. an IoT Gateway isn't about picking the "better" device. It's about picking the right tool for the job. This guide will break down the real difference, so you can make that choice with confidence.

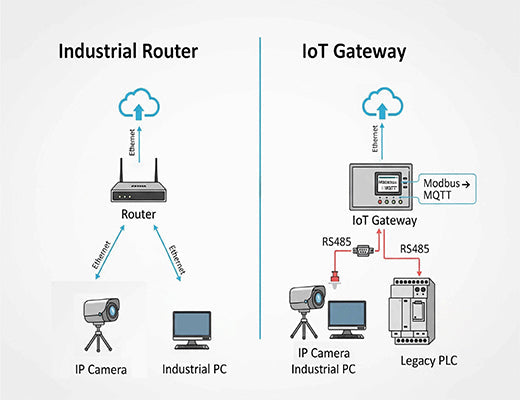
Think of an Industrial Router as a highly specialized security guard and logistics expert for your data. Its primary mission is to provide an ultra-reliable, secure, and manageable internet connection for devices that already know how to "speak" internet protocol (IP).
Its core functions are all about the quality and security of the connection itself:
If your devices (like IP cameras, modern controllers, or industrial PCs) can already connect to a standard network, the router's job is to make that connection robust, secure, and always on.
Learn More in our main guide:
The 'aha!' moment for many engineers is realizing that not all industrial equipment speaks IP. Billions of legacy devices on factory floors and in the field speak different languages—industrial protocols like Modbus RTU, Profinet, or BACnet.
This is the gateway's first superpower: protocol conversion . It can connect directly to a legacy PLC via a serial (RS485) port, "listen" to the Modbus data, and translate it into a lightweight, modern format like MQTT before sending it to the cloud. It bridges the gap between the old world of Operational Technology (OT) and the new world of Information Technology (IT).
The second superpower, found in more advanced devices often called "Edge Gateways," is local processing . Instead of just forwarding all data, a true edge gateway has a powerful processor (like a quad-core ARM CPU), more memory, and an open operating system (like RobustOS Pro, which is based on Debian).
This allows it to:
Feature |
Industrial Router |
IoT Gateway |
Primary Function |
Provide secure, reliable connectivity |
Connect devices, translate data , and process locally |
Connects to... |
IP-based devices (Cameras, PCs) |
IP-based devices AND non-IP devices (Serial PLCs, meters) |
Key Capability |
VPNs, Firewall, Failover |
All router capabilities PLUS Protocol Conversion, Edge Computing |
Best For... |
Reliable internet for modern assets, network backup, in-vehicle Wi-Fi |
Connecting legacy factory equipment, smart building automation, predictive maintenance |

Still unsure? Ask yourself these three simple questions.
The debate over Industrial Router vs. IoT Gateway isn't about which is better—it's about which is right for you.
A router is the specialist, the master of providing an unbreakable, secure connection. A gateway is the generalist, a powerful all-in-one platform that provides that same great connection but adds the intelligence to speak to any device and process data on the fly.
By understanding this key difference and asking the right questions about your application, you can confidently select the right tool and build a foundation for a successful, scalable, and reliable IIoT deployment.

A1: Yes, absolutely. All IoT Gateways include the full networking, firewall, and VPN functionalities of an Industrial Router. Think of the router's capabilities as the "base model" that every gateway is built upon.
A2: You need an "Edge" Gateway—one with powerful processing capabilities—when you have a clear need to analyze or act on data locally and in real-time. The three main drivers are: reducing latency for fast machine control, saving cellular data costs by filtering information, and running AI models for applications like predictive maintenance.
A3: Think of a protocol as the "language" a device speaks. Your laptop speaks "IP" (Internet Protocol) to communicate over the internet. Many industrial devices, however, speak older, more specialized languages like "Modbus." A gateway's job is to be a multilingual translator between these different languages.