IoT Gateway vs IoT Router: What's the Real Difference?
|
|
Time to read 5 min
|
|
Time to read 5 min
In the world of IoT, the terms "router" and "gateway" are often used interchangeably, but they represent fundamentally different functions.
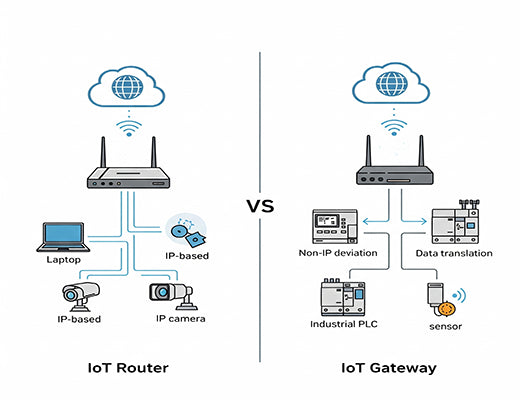
So, what's the real story in the IoT Gateway vs Router debate? In short, a router connects trusted devices on a common network to the internet, while a gateway acts as a sophisticated translator and bridge for disparate or non-IP based devices.
This guide will dive deep into this comparison, exploring the specific roles of an IoT router and how an IoT Gateway evolves into a powerful Edge IoT Gateway . By the end, you'll understand the critical differences and know exactly which device your project needs.
I can't tell you how many times I've had conversations with project managers who say, "I just need a router to get my sensors online." The reality is, what they often need is something far more capable. Choosing the wrong device is one of the most common early mistakes that can derail an IoT project, leading to security vulnerabilities and integration nightmares.
The IoT Gateway vs Router discussion isn't just about semantics; it's about understanding two distinct roles. A router is like a traffic cop for a highway where all the cars (devices) already speak the same language (IP). An IoT Gateway, on the other hand, is like a United Nations translator at a border crossing; it connects different worlds that speak entirely different languages. Let's be clear: selecting the right one is fundamental. This guide will break it down for you.

Internet Connectivity: Its main purpose is to provide a reliable internet connection, often with features like Dual-SIM failover for network resilience. This is the core function of both an Industrial 4G Router and an Industrial 5G Router .
Network Address Translation (NAT): It manages a private local network, allowing multiple devices to share a single public IP address. A powerful Industrial NAT Router like the Robustel R2111 can perform advanced NAT functions to solve common factory network problems.
Security (Firewall & VPN): It acts as a firewall, protecting the devices on its LAN from the public internet. It also functions as a powerful VPN client, creating secure, encrypted tunnels back to a corporate network using protocols like IPsec or OpenVPN.
You need an IoT Router when your primary goal is to provide simple, secure internet connectivity to devices that already speak IP . For example, connecting an industrial PC, a modern PLC with an Ethernet port, or a set of IP cameras to the internet over a cellular network.
Many industrial devices, especially in the OT world, do not speak TCP/IP. They use industrial protocols like Modbus , OPC UA, BACnet, or LoRaWAN . These devices cannot be connected directly to a standard router.
An IoT Gateway acts as the essential translator. It can communicate directly with these devices via its industrial interfaces (like RS485 or a LoRa radio), collect the data, understand it, and then translate it into a standard IT protocol like MQTT . It then sends this translated data to the cloud. This ability to bridge the OT and IT worlds is the defining feature of an IoT Gateway.
Modern industrial gateways have evolved even further. They aren't just translators; they are powerful on-site computers. This more advanced category is known as an IoT Edge Gateway or Edge IoT Gateway .
An Edge IoT Gateway has a powerful processor, more RAM, and a flexible operating system (like Debian-based RobustOS Pro). This allows it to perform edge computing , which means it can:
Analyze data locally: Run analytics or AI models to detect anomalies in real-time.
Filter data: Send only valuable insights to the cloud, saving massive bandwidth costs.
Operate autonomously: Run local control logic even if the internet connection is lost.
A prime example is the Robustel EG5120 , which combines all these capabilities into a single device.

Feature |
IoT Router |
IoT Gateway (Basic) |
IoT Edge Gateway |
Primary Function |
Provides Internet Connectivity |
Connects & Translates |
Connects, Translates & Processes |
Protocols Handled |
IP-based (TCP/IP, HTTP) |
IP + Non-IP (e.g., Modbus, LoRaWAN) |
IP + Non-IP + Custom Apps |
Onboard Processing |
Low (for routing/firewall) |
Medium (for protocol conversion) |
High (for edge analytics, Docker) |
Ideal Use Case |
Connecting IP cameras, PCs |
Connecting Modbus sensors to cloud |
Real-time factory automation |

The IoT Gateway vs Router debate is simple once you understand their roles. If you just need to provide a secure internet connection to IP-speaking devices, an IoT Router is the right tool.
However, if you need to connect industrial devices that use protocols like Modbus or LoRaWAN, you need an IoT Gateway . And if your application demands real-time local processing, analytics, and maximum reliability, then a powerful Edge IoT Gateway like the Robustel EG5120 is the clear choice. It provides not only connectivity and translation but also a future-proof platform for building truly intelligent industrial solutions.
A1: Yes, absolutely. An IoT Edge Gateway has all the functionality of an advanced industrial router (NAT, Firewall, VPNs) and adds protocol translation and edge computing capabilities on top.
A2: It's the process of converting data from one communication format to another. For example, reading a temperature value from a sensor using the Modbus RTU protocol over a serial line and then converting that value into a JSON payload to be sent over the internet using the MQTT protocol.
A3: You need an Edge IoT Gateway when you have a requirement for low-latency decision-making, need to reduce data transmission costs by processing data locally, or require your system to continue operating even if the internet connection is lost.