A Guide to In-Vehicle Connectivity for Logistics and Public Transit
|
|
Time to read 5 min
|
|
Time to read 5 min
Reliable in-vehicle connectivity is the engine driving the future of logistics, public transit, and emergency services. This guide explains why standard routers fail in a mobile environment and breaks down the essential features of a true in-vehicle industrial router—from E-Mark certification and wide voltage tolerance to intelligent software like dual SIM failover and Smart Roaming that ensure an unbreakable connection on the move.
A vehicle is one of the harshest environments for electronics due to constant vibration, extreme temperatures, and unstable power.
Purpose-built in-vehicle routers with E-Mark certification are required for safety and regulatory compliance in many automotive applications.
Uninterrupted connectivity is the primary challenge. Software like dual SIM failover and Smart Roaming is critical for maintaining a stable connection as a vehicle moves between different cellular coverage areas.
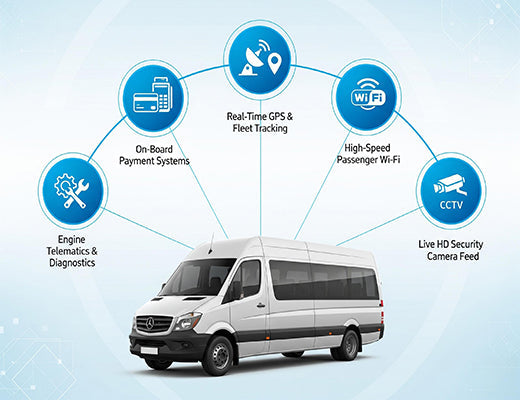
Modern in-vehicle connectivity goes beyond simple GPS tracking; it's a platform for passenger Wi-Fi, real-time telematic data, and life-saving communication for first responders.
I was speaking with a fleet manager for a large logistics company. They had tried to save money by installing cheap, consumer-grade 4G hotspots in their trucks for GPS tracking. Within six months, over half of them had failed. They rattled apart from the constant vibration, and the unstable vehicle power fried their delicate circuits.
It was a classic case of using the wrong tool for the job. A vehicle is a data center on wheels, but it's also a brutal environment. Let's be clear: providing reliable in-vehicle connectivity requires specialized hardware and intelligent software designed to handle the unique challenges of being constantly on the move.
This guide will break down what to look for in a professional solution that won't let you down when it matters most.

Why can't you just use a standard router in a truck or a bus? Because a vehicle is actively trying to destroy your electronics.
A moving vehicle is the ultimate connectivity challenge, constantly passing through areas of strong and weak cellular coverage.

A modern connected vehicle platform enables a wide range of services that deliver a clear return on investment.

Professional in-vehicle connectivity is about so much more than a dot on a map. It's about building a reliable, secure, and manageable mobile network that serves as the foundation for a new generation of services. By choosing a ruggedized, certified industrial router with intelligent connectivity software, you are investing in a platform that will keep your fleet online, your passengers happy, and your critical operations running, no matter where the road takes you.
Learn More in our main guide:
A1: E-Mark is a type-approval certification for automotive electronic components and vehicles sold in the European Union and other regions that adhere to UN ECE regulations. It certifies that the device meets strict standards for electromagnetic compatibility, safety, and environmental protection, ensuring it will not interfere with the vehicle's critical systems.
A2: You use a centralized cloud management platform like RCMS. It allows you to configure, monitor, and manage the passenger Wi-Fi service across your entire fleet from a single web interface. You can set data limits, customize the login portal (captive portal), and even implement content filtering.
A3: For vehicles, it's best to use a low-profile, multi-antenna combination ("combo") antenna that is permanently mounted to the roof of the vehicle. These rugged antennas typically combine multiple cellular, Wi-Fi, and GPS/GNSS antennas into a single, aerodynamic housing, providing the best possible performance and durability.