Adaptive Machining: How Edge Control Can Optimize CNC Router Performance in Real-Time
|
|
Time to read 5 min
|
|
Time to read 5 min
This guide explores the cutting edge of CNC router optimization: adaptive machining powered by edge control. Unlike traditional machining which uses fixed feed rates, adaptive control uses real-time sensor data to continuously adjust cutting parameters on the fly. By deploying an intelligent edge gateway to monitor conditions like spindle load and instantly optimize the feed rate, adaptive cnc control pushes your machine to its maximum safe limit, dramatically reducing cycle times while extending tool life.
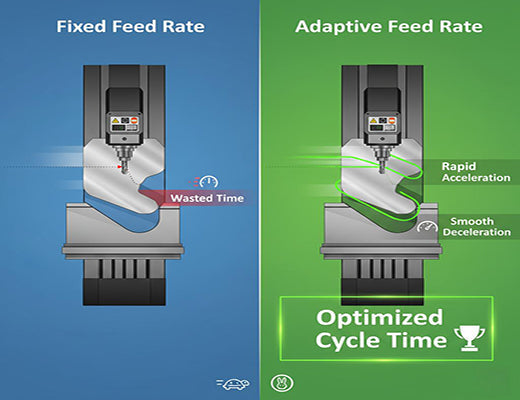
Traditional CNC router programs use conservative, fixed feed rates to handle the "worst-case scenario" cut, wasting time during lighter cuts.
Adaptive machining uses edge control to create a real-time feedback loop, monitoring actual cutting conditions and adjusting the feed rate dynamically.
The primary benefits are significantly reduced cycle times (often 20-50% faster) and improved tool life by maintaining a consistent chip load.
This requires a high-performance edge gateway capable of analyzing data and sending override commands to the CNC router controller in milliseconds.
Watch a typical CNC router program run. You'll notice the cutting tool often moves at the same relatively slow speed, whether it's plunging into thick material or just skimming the surface. Why? Because the programmer had to choose a single, safe feed rate that could handle the toughest part of the cut without breaking the tool. This means for much of the program, the machine is running far slower than it safely could be. It's like driving your car in first gear on the highway just because there might be a traffic jam ahead.
What if your CNC router could have the intelligence to "put the pedal down" during easy cuts and automatically ease off when the going gets tough?
Let's be clear: it can. This intelligent, dynamic optimization is called adaptive machining, and it's made possible by the real-time decision-making power of edge control.

A G-code program typically defines a fixed feed rate (the 'F' value) for each cutting move. This rate must be conservative enough to handle the maximum anticipated cutting force. This leads to massive inefficiencies:
This "sense-decide-act" loop runs hundreds or thousands of times per second, constantly fine-tuning the machine's speed to maintain the optimal cutting force.

The results of implementing adaptive cnc control can be dramatic:

Adaptive machining powered by edge control is a leap beyond static programming. It gives your CNC router the intelligence to optimize its own performance in real-time, adapting to the unique conditions of every cut. By implementing this closed-loop system with a high-performance edge gateway, you can safely push your machines closer to their true limits, unlocking significant gains in speed, efficiency, and profitability that were previously unattainable.
A1: The controller needs to support two key things: 1. Provide real-time spindle load data (or allow connection of external sensors). 2. Accept real-time feed rate override commands. Most modern industrial controllers (Fanuc, Siemens, Haas, Heidenhain, etc.) support these functions, often via Ethernet APIs or standard fieldbus protocols.
A2: Yes, a powerful industrial edge gateway like the EG5120 is specifically designed for this. Its multi-core ARM processor can easily run the optimization algorithm and communicate with the CNC controller with the required millisecond-level latency.
A3: Specialized CAM software packages often include adaptive toolpath strategies. Implementing a real-time adaptive control loop at the edge, however, typically requires developing or integrating specific application logic on the edge gateway. While this requires technical expertise, the potential ROI in cycle time reduction often justifies the investment quickly, especially in high-volume production. Open platforms like the EG5120 offer flexibility in how this logic is implemented (e.g., using Python or specialized partner software).