Case Study: How LoRaWAN for Smart Buildings Bridges the Gap with Legacy BACnet Systems
|
|
Time to read 4 min
|
|
Time to read 4 min
Upgrading a commercial building's control systems often seems like an impossible task, caught between the high cost of rewiring and the limitations of legacy protocols like BACnet.
This case study explores a powerful and cost-effective solution: using LoRaWAN for smart buildings .
We'll walk through a real-world scenario showing how a modern BACnet LoRaWAN gateway can seamlessly integrate new, wireless sensors with an existing Building Management System (BMS), unlocking new efficiencies in energy management and occupant comfort without a disruptive overhaul.
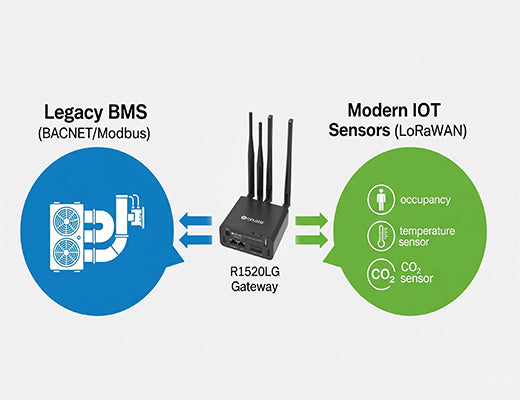
I've spoken with dozens of facility managers who all share the same frustration. They manage a building with a rock-solid, 20-year-old Building Management System (BMS) that controls the core HVAC. It works, but it's a closed island. They want to add new sensors to monitor room occupancy, CO2 levels, or water leaks, but the thought of running hundreds of meters of new cable through walls and ceilings is a non-starter—it's simply too expensive and disruptive.
This is where so many smart building projects die. But what if you could deploy hundreds of battery-powered sensors wirelessly and have them talk directly to your old BACnet system? This isn't a futuristic dream; it's a practical solution enabled by a new class of intelligent gateways. This case study will show you how LoRaWAN for smart buildings is the key to unlocking your legacy system's hidden potential.

Our scenario is a typical 10-story office building with an existing BMS that uses the BACnet protocol to control its main air handling units. The goal is to improve energy efficiency by adjusting airflow based on real-time occupancy and CO2 levels in individual meeting rooms—data the current system doesn't have. This is a classic challenge for LoRaWAN for smart buildings .
The solution is to deploy an intelligent BACnet LoRaWAN gateway that acts as a universal translator. This approach is central to successful projects using LoRaWAN for smart buildings .
The Robustel R1520LG is perfectly suited for this role. It's not just a LoRaWAN gateway; it's a LoRaWAN edge gateway with a Debian-based OS, giving it the power to process data locally.
Here’s how the solution is implemented:
{"occupancy": true, "co2": 850}), and translates it into BACnet objects.
By implementing this LoRaWAN for smart buildings solution, the facility manager achieved all their goals:
This case study demonstrates that you don't need to choose between your reliable legacy systems and the benefits of modern IoT technology. A powerful BACnet LoRaWAN gateway acts as the perfect bridge, allowing you to layer new capabilities on top of your existing infrastructure. This approach to LoRaWAN for smart buildings is faster, more affordable, and less disruptive, providing the smartest path to a truly intelligent and efficient building.

A1: BACnet (Building Automation and Control Networks) is a communication protocol that is the global standard for building automation. It allows devices from different manufacturers, such as HVAC, lighting, and security systems, to communicate with each other.
A2: Yes. A flexible LoRaWAN edge gateway can run different protocol translation applications. It can be configured to output data in other common industrial protocols like Modbus TCP, making it compatible with a wide range of legacy systems.
A3: Yes. By creating a private LoRaWAN network on the gateway, your sensor traffic is encrypted and never exposed to the public internet. The gateway itself can then connect to the BMS over a secure, isolated local network, providing a robust, multi-layered security architecture.