Building Smarter Cities with Edge Control: From Traffic to Public Safety
|
|
Time to read 4 min
|
|
Time to read 4 min
This guide explains how edge control is the key technology for building truly "smart" cities, moving beyond passive monitoring to active, real-time automation. By deploying intelligent edge gateways at the roadside, cities can implement autonomous systems for adaptive traffic management and proactive public safety. This decentralized approach solves the critical challenges of latency and cost, enabling a new generation of responsive, resilient, and efficient urban infrastructure.
Edge control in a smart city context means placing a powerful "brain" at the intersection or on the street corner to make instant, local decisions.
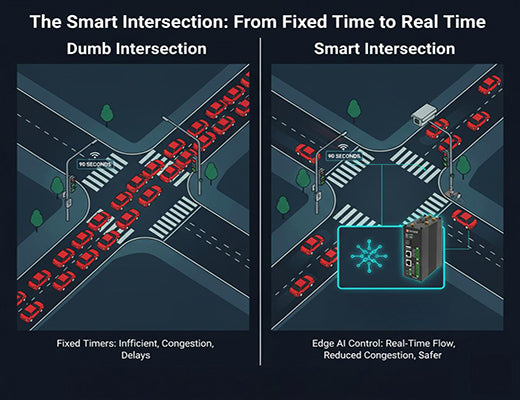
It transforms traffic systems from running on fixed timers to adapting to real-world vehicle and pedestrian flow in real-time.
For public safety, it enables AI-powered cameras to not just record events, but to autonomously detect incidents and trigger immediate on-site responses.
The entire system relies on rugged, high-performance edge gateways that can survive harsh roadside environments and run complex AI logic locally.
I'm sure you've had this thought while sitting at a red light at 3 a.m. with absolutely no cross-traffic: "Why isn't this traffic light smarter?" For years, our urban infrastructure has been "dumb"—operating on fixed schedules and reacting to problems only after they've happened.
The first wave of "smart city" technology was about monitoring—installing thousands of cameras and sensors to send data back to a central control room. But this created two new problems: a tidal wave of data that was too expensive to transmit, and a network delay (latency) that made real-time control impossible.
Let's be clear: a city doesn't get smarter by just watching. It gets smarter by acting. The technology that enables this instant, local action is edge control.

A centralized, cloud-based approach to city management is fundamentally flawed. Edge control solves these flaws by distributing intelligence.
This is the most impactful application for transforming urban mobility.
This transforms a city's surveillance network from a passive recording tool into an active, automated security guard.

Edge control is the technology that makes the promise of the smart city a practical reality. It moves our urban infrastructure from a state of passive monitoring to one of active, intelligent, and autonomous operation. By deploying powerful, rugged, and AI-capable edge gateways like the EG5120 at the roadside, cities can build traffic systems that think, security systems that see, and public services that react—all in real-time, creating a safer, more efficient, and more livable environment for everyone.
Further Reading:
What is Edge Control? The Future of Real-Time Industrial AutomationA Buyer's Guide to Edge Products: Choosing the Right Hardware for Your ApplicationPowering the Future: How Edge Control is Revolutionizing the Smart Grid
A1: This is a critical consideration. The hardware must be "ruggedized," which means it needs a wide operating temperature range (e.g., -40 to +70°C) to survive hot summers and cold winters, a high level of EMC immunity to resist electrical noise, and a fanless, durable metal enclosure to protect against dust and vibration.
A2: Yes, a professional edge control architecture is highly secure. The edge gateway acts as a hardened firewall. All non-essential ports are disabled, and any communication with the central management platform is sent over a heavily encrypted VPN tunnel. Choosing a vendor with a certified secure development lifecycle (like IEC 62443) is essential.
A3: A cloud management platform like RCMS is non-negotiable for managing a city-wide deployment. It allows city IT staff to remotely monitor the health and connectivity of every gateway, diagnose problems, and, most importantly, securely push out updates to the AI models and control logic running on the devices.