A Deep Dive into IoT Edge Devices
|
|
Time to read 6 min
|
|
Time to read 6 min
This guide provides a deep dive into the world of iot edge devices.
We explore the different types of edge computing hardware, from smart sensors to powerful iot edge gateway solutions and dedicated industrial edge devices.
Using the Robustel EG5120 as a real-world example, we break down the critical components—like ARM processors and NPUs for edge ai hardware—and provide a clear framework for choosing the right device for your industrial needs.
In our ultimate guide, we explained what edge computing is. Now, let's get tangible. How does this powerful concept actually come to life in the real world? The answer lies in a special category of hardware: iot edge devices. These aren't your standard desktop computers or servers. They are the rugged, intelligent, and highly specialized workhorses that form the physical foundation of any edge computing strategy. Choosing the right device is paramount; it’s the difference between a successful IIoT deployment and a project plagued by failure. So, let's pull back the curtain and explore the fascinating world of edge computing hardware.
Let’s be clear, an iot edge devices is any piece of hardware with enough onboard processing power to analyze data locally, at the "edge" of the network, right where the data is created. This is a fundamental shift from the past, where "dumb" sensors would simply collect data and pass it on to a centralized cloud for all the heavy lifting.
The "aha!" moment for many engineers is realizing that the value of iot edge devices isn't just in collecting data, but in understanding it. An iot sensor might tell you a motor's temperature is 85°C. But an intelligent edge device can take that data, compare it to the last 1,000 hours of operation, factor in the current production load, and determine that this temperature reading is an anomaly that signals a likely bearing failure within the next 48 hours. That's the power of local intelligence.
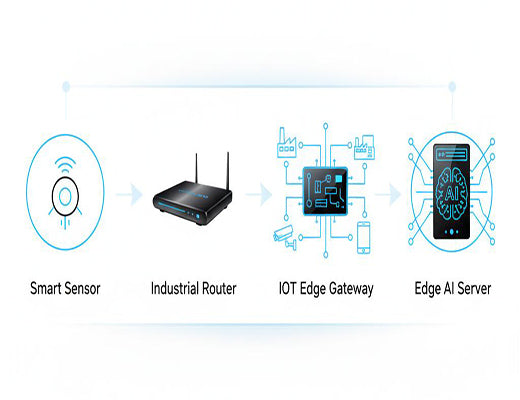
The term iot edge devices covers a broad range of hardware. In my experience, they generally fall into four key categories, each serving a different purpose.
plc to MQTT for the cloud. [Internal Link: Link to 'How to Choose the Best Industrial 5G Router' article]IoT Edge Gateway (The Central Hub) This is the most common and versatile type of industrial edge device. An iot edge gateway acts as a central aggregator and processing hub for multiple downstream sensors and machines. It's a powerful, purpose-built computer designed to collect data from various sources, process it locally, and manage communications with the cloud. Industrial Edge Devices with AI Acceleration (Edge Servers) At the highest end of the spectrum, you have powerful industrial edge devices, sometimes called edge server hardware. These devices, equipped with multi-core processors and dedicated NPUs (Neural Processing Units), are designed specifically for demanding edge ai hardware workloads like real-time video analysis or running complex machine learning models.
To truly understand what makes these devices tick, let's break down a state-of-the-art example. A device like the Robustel EG5120 isn't just a collection of parts; it's an integrated system where each component is chosen for performance in harsh industrial environments.
The heart of the EG5120 is a powerful quad-core arm processor (the NXP i.MX 8M Plus), which provides the raw power for running complex applications. But its real secret weapon is the integrated 2.3 TOPS npu. This dedicated AI accelerator allows the device to run sophisticated machine learning models with incredible efficiency, making true edge ai hardware accessible for mainstream industrial applications.
Hardware is useless without flexible software. The most capable industrial edge devices run open, Linux-based operating systems. The EG5120 runs RobustOS Pro, which is based on Debian 11. This gives developers immense freedom and access to a vast ecosystem of open-source tools. Crucially, it supports docker, allowing any application to be packaged into a container and deployed seamlessly, a feature that dramatically accelerates development and ensures scalability.
An iot edge gateway must be able to speak the language of the factory floor. This means providing a rich set of physical interfaces beyond a simple Ethernet port. Essential I/O includes:

Navigating the market for iot edge devices can be daunting. Here’s a simple three-step framework to guide your decision.
Learn More:
What is Edge Computing in IoT? The Ultimate Guide

The main types include smart sensors with basic onboard processing, industrial routers with some edge capabilities, versatile IoT edge gateways that act as central hubs for multiple machines, and high-performance industrial edge computers or servers designed for demanding AI workloads.
An IoT sensor is typically designed to measure a single physical property (like temperature or pressure). A modern iot edge gateway is a more powerful computer designed to connect to multiple sensors and devices, aggregate their data, process it locally, and manage communication with other networks or the cloud.
First, define your computational requirements (e.g., simple data aggregation vs. complex AI). Second, assess the physical operating environment to determine the necessary level of ruggedization. Third, ensure the device is supported by a powerful remote management platform to allow for scalable deployment and maintenance.