What is an IoT Gateway? A 2025 Guide to Edge vs. Cloud
Summary
The term "IoT Gateway" is fundamental to understanding how the Internet of Things works, yet its role is often misunderstood. So, what is an IoT Gateway? At its core, an IoT Gateway is a physical device or software program that serves as the crucial connection point between IoT devices/sensors and the cloud.
This guide will provide a comprehensive definition, explaining the key functions of an IoT Gateway , such as protocol translation and security.
Furthermore, we will explore the critical evolution of this technology, comparing a standard, cloud-reliant IoT Gateway with a modern, powerful Industrial IoT Edge Gateway , and introduce the Robustel EG5120 as a prime example to illustrate these concepts.
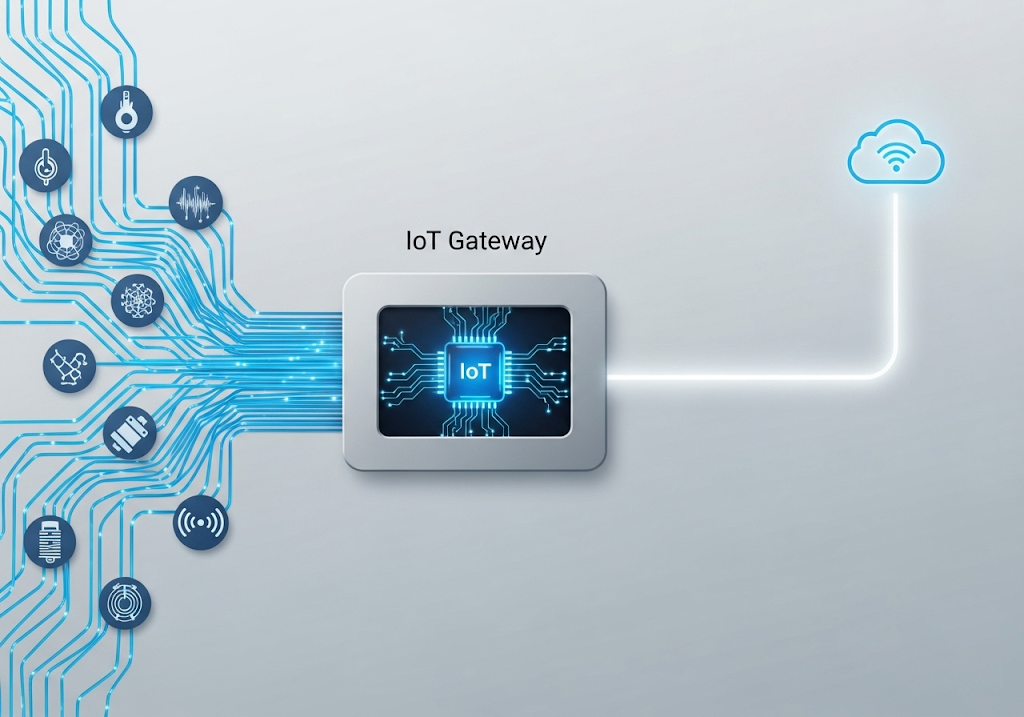
Introduction: The Bridge Between the Physical and Digital Worlds
The Internet of Things (IoT) has connected billions of physical devices to the internet, enabling them to collect and share data. However, these devices—sensors, actuators, and machines—often use low-power, short-range communication protocols like Zigbee, Bluetooth, or industrial protocols like Modbus, which cannot connect directly to the internet. This is where the IoT Gateway comes in.
Think of an IoT Gateway as a multilingual translator and a smart traffic controller for your "things." It aggregates data from various local devices, translates their different languages (protocols) into a standard internet-friendly language (like MQTT or HTTPS), and then securely transmits that data to the cloud for processing and analysis. As IoT solutions become more advanced, the role of the gateway has evolved significantly with the rise of edge computing, creating a distinction between standard gateways and more intelligent edge gateways.
What is an IoT Gateway ? The Core Definition and Functions
Key Functions of an IoT Gateway
- Connectivity and Protocol Translation: The most fundamental role of an IoT Gateway is to bridge different communication technologies and protocols. It collects data from devices using protocols like Modbus, OPC UA, BLE, or LoRaWAN and translates it into standard IP-based protocols like MQTT, CoAP, or HTTPS that cloud platforms can understand.
- Device Connectivity & Management: It manages the connections to and from local IoT devices, handling authentication and authorization to ensure only trusted devices can join the network.
- Security: An IoT Gateway acts as a critical line of defense, protecting the local device network from the public internet. It can implement firewall rules, access control lists, and create secure, encrypted communication tunnels (like VPNs) to the cloud, safeguarding sensitive data.
- Data Filtering and Buffering: It can filter out redundant or unnecessary data before sending it to the cloud, and it can buffer data locally if the internet connection is temporarily lost, preventing data loss.
How an IoT Gateway Works: The Data Journey
The process of moving data from a sensor to the cloud via an IoT Gateway typically follows these steps:
- Data Aggregation: The IoT Gateway collects data streams from multiple sensors and devices in its vicinity. For example, in a factory, it might collect temperature data from a Modbus sensor and status data from a PLC.
- Protocol Conversion: It then translates these various protocols into a single, common format, like MQTT with a JSON payload. This standardizes the data.
- Data Transmission: Finally, it uses its WAN connection (which could be Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or cellular) to securely send the standardized data to a cloud platform for storage, analysis, and visualization.
The Evolution: Standard IoT Gateway vs. Industrial IoT Edge Gateway
The Standard (or "Cloud-Reliant") IoT Gateway
A standard IoT Gateway primarily acts as a data forwarder. It performs the essential tasks of protocol translation and data transmission, but most of the "thinking"—data processing, analytics, and decision-making—happens in the cloud.
-
Limitations:
- Latency: There is a delay as data travels to the cloud and back for a decision.
- Bandwidth Costs: Sending all raw data to the cloud can be expensive, especially over cellular.
- Cloud Dependency: If the internet connection fails, the system's "intelligence" is cut off.
The Modern Industrial IoT Edge Gateway
The Industrial IoT Edge Gateway is the next generation of this technology. It is an IoT Gateway , but with a powerful onboard computer (processor, RAM, storage) that enables edge computing . Edge computing means processing data locally, at the "edge" of the network, closer to where it is created.
Key Advantages of an Edge Gateway:
- Reduced Latency: Real-time decisions can be made locally in milliseconds without a round-trip to the cloud.
- Lower Bandwidth Costs: By analyzing, filtering, and aggregating data locally, the edge gateway only sends essential or summarized information to the cloud, saving significant costs.
- Increased Reliability & Offline Operation: An Industrial IoT Edge Gateway can run automation rules and process data autonomously, even if the connection to the cloud is lost.
- Enhanced Security: Sensitive data can be processed on-site without ever having to be transmitted over the internet, which is crucial for privacy and security.

An Example of a Powerful Industrial IoT Edge Gateway : The Robustel EG5120
High-Performance Hardware and Rich Connectivity
Open and Flexible Programming Environment
Enterprise-Grade Security and Reliability
Simplified Cloud Management
The EG5120 fully integrates with the Robustel Cloud Manager Service (RCMS) , a powerful platform for monitoring and managing your entire fleet of gateways. This allows for centralized OTA updates (for both the OS and containerized applications) and secure remote access to the gateway and its connected end devices, which dramatically reduces operational costs.
EG5120 Key Specifications Summary:
| Feature Category | Specification |
|---|---|
| System | |
| CPU | Quad-Core ARM Cortex-A53, 1.6 GHz (NXP i.MX8) |
| RAM / Storage | 2 GB DDR4 / 16 GB eMMC |
| Connectivity | |
| Cellular | Global 4G LTE Cat 4 (Dual SIM Failover) |
| Ethernet | 2 x Gigabit Ethernet (10/100/1000 Mbps) |
| Industrial Interfaces | 2 x RS232/RS485, 2 x DI, 2 x DO |
| Software | |
| Operating System | RobustOS Pro (Debian 11 based with LTS) |
| Containerization | Docker support |
| Key Software Support | Node-RED, MQTT, InfluxDB, Grafana, Modbus, OPC UA, BACnet, etc. |

Conclusion: The Edge Gateway in IoT is the Cornerstone of Modern IIoT
An IoT Gateway is a foundational component of any IoT system, but for serious industrial applications, an Industrial IoT Edge Gateway is essential. It is a powerful, intelligent computer that serves as the secure bridge between the physical and digital worlds, enabling real-time local processing, enhancing reliability, lowering operational costs, and providing the multi-layered security needed for demanding applications. As IoT continues to expand, the role of the industrial IoT edge gateway will only become more critical. Devices like the Robustel EG5120, with their high-performance processors, open Debian-based OS, and integrated cloud management, represent the future of intelligent and scalable IoT deployments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the main difference between an IoT Gateway and a standard internet router?
A1: A standard router's primary function is to forward IP data packets between networks. An IoT Gateway does this but also performs the critical function of protocol translation, converting non-IP based protocols (like Modbus, Zigbee, etc.) into IP-based protocols (like MQTT) that the internet and cloud platforms can understand.
Q2: Can I run custom applications on an industrial IoT edge gateway?
A2: Yes, on advanced gateways like the Robustel EG5120. It supports Docker, allowing you to deploy applications written in almost any language (C, C++, Python, Java, Go, Node.js, etc.) inside containers. This provides incredible flexibility for custom edge analytics and control logic.
Q3: Is an industrial IoT edge gateway secure?
A3: Security is a core function of an industrial IoT Gateway . They are designed to be a secure buffer between OT and IT. Features like a stateful firewall, extensive VPN support (IPsec, OpenVPN, etc.), and a hardened operating system like RobustOS Pro (which is certified to IEC 62443-4-1) are essential. Furthermore, RobustOS Pro undergoes rigorous, independent penetration testing annually to validate its resilience against real-world threats.





Leave a comment