Real-Time Quality Control: Using Edge AI and Vision in Smart Factories
|
|
Time to read 5 min
|
|
Time to read 5 min
Edge AI is revolutionizing quality control in smart factories by bringing the power of machine learning directly to the production line. By using a powerful industrial edge gateway equipped with a dedicated Neural Processing Unit (NPU), manufacturers can now perform complex machine vision analysis in real-time. This guide explains how this technology works, enabling 100% automated, high-speed defect detection that improves product quality, reduces waste, and boosts overall production efficiency.
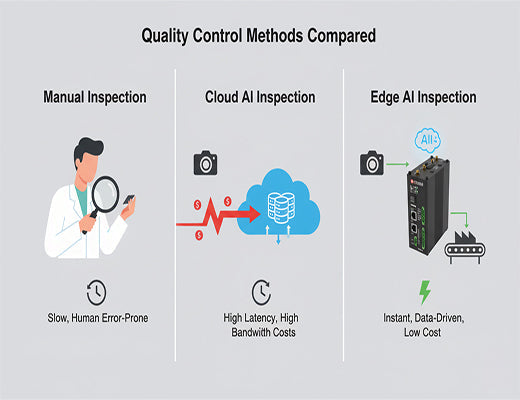
Traditional quality control methods—both manual and cloud-based—are often too slow, inconsistent, or expensive for the demands of modern, high-speed manufacturing.
Edge AI solves this by running artificial intelligence models (inference) locally on an edge gateway, enabling instant, millisecond-level decision-making right on the factory floor.
The key enabling hardware is a dedicated NPU (Neural Processing Unit), a specialized processor on the gateway that dramatically accelerates AI calculations.
The result is a fully automated quality control system that is faster, more accurate, and more reliable than a human inspector.
I was visiting a modern electronics assembly plant, watching a fast-moving conveyor belt where hundreds of small components zipped by every minute. At the end of the line sat a human inspector, staring intently at each part, trying to spot microscopic defects. He was a professional, but I couldn't help but think: he's only human. He blinks. He gets tired. He's going to miss things.
This is the classic quality control dilemma. Manual inspection is slow and prone to error. But the alternative, sending high-resolution video streams to the cloud for AI analysis, is often too slow and expensive due to latency and massive bandwidth costs.
Let's be clear: there is now a third, far superior option. The solution is to bring the AI to the camera, not the other way around. The solution is Edge AI.

In simple terms, Edge AI is the practice of running an Artificial Intelligence model's "inference" (the process of making a prediction) directly on a local hardware device at the "edge" of the network, rather than in a distant cloud data center.
This is a perfect match for machine vision applications for two critical reasons:
Edge AI solves both problems by keeping the entire process—capturing the image, analyzing it, and making a decision—local.
So how can a small, rugged box on the factory floor run a complex AI model? The real 'aha!' moment for engineers is understanding the power of a dedicated NPU (Neural Processing Unit).
Think of it like this: a standard CPU is a generalist, good at many things. An NPU is a specialist. It's a purpose-built co-processor on the gateway's main chip that is designed to do one thing with incredible efficiency: execute the mathematical calculations required for AI model inference. An NPU, like the 2.3 TOPS (trillion operations per second) unit in the
Robustel EG5120, can run these models hundreds of times faster and with far less power than a general-purpose CPU. It's the special ingredient that makes real-time Edge AI possible.

If the AI model detects a defect, the gateway doesn't just send an alert. It takes immediate action. It can use its built-in Digital I/O (DO) ports to instantly trigger a rejection mechanism on the production line, such as a pneumatic pusher or a diverter gate, to remove the faulty part from the line.

Edge AI for real-time quality control is no longer a futuristic concept from a research lab. It's a practical, powerful, and accessible technology that is delivering a clear and immediate return on investment for manufacturers today.
By leveraging the power of a purpose-built industrial edge gateway with a dedicated NPU, factories can build automated quality control systems that are more accurate than a human inspector, faster than a cloud-based solution, and intelligent enough to drive a new era of manufacturing efficiency.
Learn more in our main guide:
A1: While the process of training a new AI model to recognize your specific products still requires data science expertise, the process of deploying a pre-trained model is becoming much easier. Using tools like Docker, a trained model can be packaged into a simple container and deployed to an edge gateway by a developer or automation engineer.
A2: An NPU, or Neural Processing Unit, is a specialized co-processor on the main chip that is specifically designed to accelerate the types of mathematical operations used by AI algorithms. It's vastly more efficient at this task than a general-purpose CPU, allowing a low-power edge device to perform real-time AI inference that would otherwise require a powerful server.
A3: You could, but a dedicated industrial edge gateway offers key advantages. It's typically smaller, more power-efficient, and ruggedized for the factory environment. More importantly, it integrates all the necessary components—the CPU, NPU, industrial I/O, and cellular connectivity—into a single, reliable device that is designed to be managed remotely as part of a large fleet.