Edge Control for LPWAN: Automating Your LoRaWAN Network with the R1520LG
|
|
Time to read 4 min
|
|
Time to read 4 min
This guide introduces a powerful new concept: Edge control for LPWAN. We'll explain how a traditional LoRaWAN network is a one-way street for data, but by using an all-in-one gateway with built-in edge computing capabilities, you can create a truly autonomous, two-way control system. We'll show how a device like the Robustel R1520LG can use data from wireless LoRaWAN sensors to make local decisions and trigger physical actions, enabling a new generation of LoRaWAN automation for smart agriculture and beyond.
Traditional LoRaWAN is for monitoring. Edge control for LoRaWAN is about adding autonomous action.
The key is a LoRaWAN gateway with edge computing capabilities, which can run a local Network Server (LNS) and custom control logic, even when disconnected from the internet.
This architecture enables a "closed loop" where the gateway can use data from a LoRaWAN sensor to either control a locally wired device (via DI/DO) or send a command (downlink) back to a LoRaWAN actuator.
This is a game-changer for building resilient, off-grid automation systems in applications like smart agriculture and environmental monitoring.
For years, the promise of LoRaWAN has been its incredible ability to listen. You can place a tiny, battery-powered sensor in the middle of a vast farm, and a gateway miles away can hear its faint whisper. It's a revolutionary technology for monitoring the unconnected world. But what if your network could do more than just listen? What if it could talk back? What if it could act?
Let's be clear: it can. The technology that transforms a passive LoRaWAN monitoring network into an active, intelligent automation system is edge control. It's about giving your LoRaWAN gateway a brain of its own.

A standard LoRaWAN network is a fantastic data collection tool, but it's a one-way street.
This works, but it's slow, and it's completely dependent on a stable internet connection.
The 'aha!' moment is realizing that you can move the "brain" (the Network Server and the control logic) out of the distant cloud and place it directly inside the gateway itself. This is what a LoRaWAN gateway with edge computing capabilities, like the Robustel R1520LG, is designed to do.
Powered by RobustOS Pro (a Debian Linux environment), the R1520LG can:
This creates a self-contained, autonomous LoRaWAN automation system that can perform the entire "sense-decide-act" loop on-site, in real-time, even with zero internet connection. This is true edge control for the low-power, wide-area world.
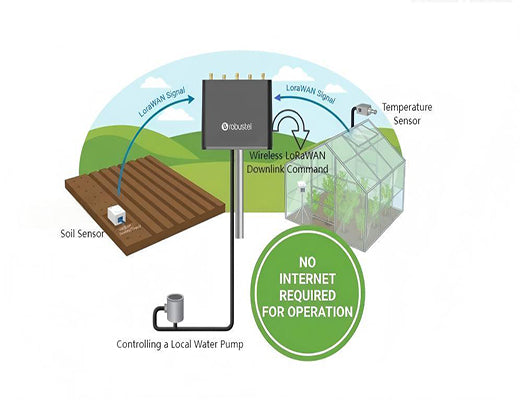
Let's imagine an off-grid greenhouse and irrigation system.
This entire system requires no cloud and no active internet connection to operate, making it incredibly resilient.

Edge control for LPWAN is a profound evolution. It transforms your LoRaWAN network from a passive data collection tool into an active, intelligent, and autonomous control system. By leveraging the unique, all-in-one capabilities of a LoRaWAN gateway with edge computing like the R1520LG, you can build incredibly resilient and efficient automation solutions for the most remote and challenging environments, turning the whispers of your sensors into decisive, intelligent action.

A1: A downlink is a message sent from the network (originating at the Network Server) down to an end device. This is how you send commands or configuration changes to your LoRaWAN sensors or actuators. The ability to generate these downlinks locally is a key feature of an edge control gateway.
A2: ChirpStack is a popular, powerful, and completely open-source LoRaWAN Network Server. It's the "brain" of the network that manages gateways and devices. A key feature of the R1520LG is that it is powerful enough to run the entire ChirpStack stack directly on the device.
A3: No. While you can write complex Python scripts, the easiest way to start is with Node-RED. It provides a visual, drag-and-drop interface where you can easily create the "IF-THEN" logic for your LoRaWAN automation flows without writing any code.