6 Key Benefits of Edge Computing for Industrial IoT (IIoT)
|
|
Time to read 6 min
|
|
Time to read 6 min
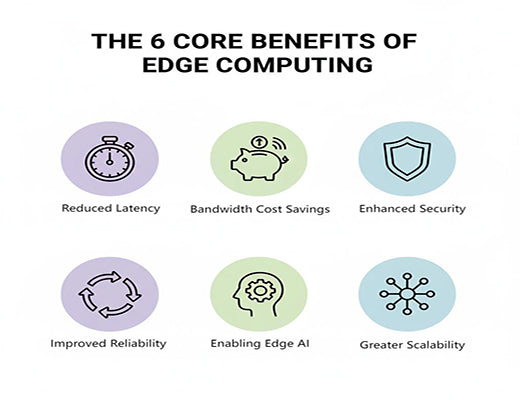
The benefits of edge computing in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) are transformative, directly addressing the biggest challenges of a cloud-only approach.
By processing data locally, edge computing dramatically reduces network latency for real-time control, slashes cellular data costs by filtering information on-site, improves operational reliability during internet outages, and enhances the security of critical assets.
Ultimately, it is the key that unlocks advanced applications like real-time AI and large-scale IoT deployments.
I was talking with an operations manager for a smart factory recently. Their goal was ambitious: to install high-resolution cameras on their production lines for real-time AI-powered quality control. They started by trying to stream all the video feeds to the cloud for analysis. The result? A pilot project that was dead on arrival. The latency was too high for real-time decisions, and their finance department calculated that the cellular data costs would be astronomical.
This story is incredibly common. The promise of IoT is often met with the harsh reality of physics and economics. The cloud is powerful, but it’s far away.
Let's be clear: the solution to this problem is to stop sending everything to the cloud in the first place. By moving intelligence to the network edge, you can unlock a host of powerful business benefits. Here are the six most critical benefits of edge computing.

reduced cellular data backhaul volume by over 80%. It’s no surprise that Gartner predicts by 2025, 75% of enterprise data will be processed outside the cloud.

The benefits of edge computing are clear, compelling, and directly tied to your bottom line. It's a strategy that makes your IoT systems faster, more cost-effective, more reliable, and more secure.
By moving beyond a simple "connect and forward" model and embracing on-site data processing, you are not just adopting a new technology. You are building a scalable and future-proof foundation for the next generation of industrial automation and intelligence.
Learn More in our main guide:

It truly depends on your application. For a manufacturer deploying real-time robotics, the most critical benefit is reduced latency. For a utility monitoring thousands of remote sites over cellular, the biggest driver is bandwidth cost savings. For a critical infrastructure application, it's often the improved reliability of autonomous operation.
No, it means you use the cloud more intelligently. The best architecture is a hybrid model where the edge handles all the immediate, real-time tasks, while the cloud is used for what it does best: long-term storage, big data analytics on aggregated insights, and centralized fleet management.
To realize the true benefits of edge computing, you need a purpose-built IoT Edge Gateway, not just a simple router. This means a device with a powerful multi-core processor, sufficient RAM and reliable eMMC storage, and an open operating system that allows you to deploy custom applications.