What is Managed Private 5G? The Ultimate Network for Industrial Edge Computing
|
|
Time to read 5 min
|
|
Time to read 5 min
Private 5G is like having your own exclusive, enterprise-grade cell network for your factory, warehouse, or campus, eliminating the issues of congestion and interference found on public networks.
Its key benefits over Wi-Fi for industrial use are superior reliability, consistently lower latency (URLLC), seamless mobility without roaming failures, and enhanced security.
Private 5G is the key network enabler for the most demanding edge computing use cases that require guaranteed, "wire-like" wireless performance.
Industrial 5G edge gateways and routers are the essential User Equipment (UE) that connect your machines, robots, and PLCs to this private network.
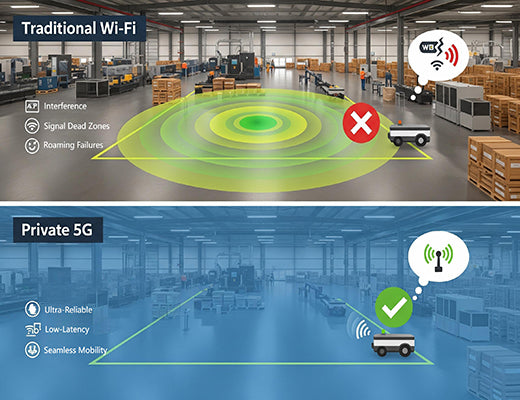
I've had the same conversation with dozens of factory managers who have invested heavily in automation. Their biggest frustration? The network. Their state-of-the-art Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs) constantly stop because of Wi-Fi dead zones. Their mobile robotics applications suffer from unpredictable latency spikes. They're trying to build the factory of the future on a network designed for the office of the past.
Let's be clear: for mission-critical industrial automation, Wi-Fi is often not good enough. You need a wireless network with the reliability and performance of a physical cable. That network is here, and it's called Private 5G.
This guide will explain what a private 5G network is and why its partnership with edge computing is the definitive blueprint for the next generation of industrial automation.

For years, Wi-Fi has been the default wireless technology. But in large, harsh, and mobile-centric industrial environments, its limitations become critical pain points:
A Private 5G network solves all of these problems. It is a localized, privately owned and operated 5G "bubble" that you control completely, using dedicated, licensed, or shared spectrum (like CBRS in the US).
Private 5G and edge computing are not separate technologies; they are two sides of the same coin. They are the perfect partners for building the factory of the future.
You need both to win. The guaranteed low latency and high bandwidth of the private network allow the edge gateway to perform its real-time analytics and control functions with the maximum possible reliability. This combination is what allows a fleet of AGVs to operate flawlessly or a real-time AI quality control system to function without error.

How do your PLCs, robots, and sensors actually connect to this new private network? They connect through a piece of hardware called User Equipment (UE). In an industrial context, the UE is a rugged and reliable Industrial 5G Gateway or Router.
The role of the gateway is to act as the on-ramp for all your OT assets. It communicates with the private 5G network wirelessly and provides standard Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and serial ports for your industrial equipment to plug into.

The combination of Private 5G and edge computing is the definitive blueprint for the next generation of smart factories, automated ports, and intelligent industrial sites. While Wi-Fi will continue to have its place for non-critical applications, for the mission-critical operations that define Industry 4.0, a private cellular network provides the ultimate in wireless performance, security, and control. By choosing robust, industrial-grade 5G edge gateways to connect your assets, you can fully unlock the potential of this transformative infrastructure.
Learn more in our main guide:
A1: Private 5G is the technology—the on-premise cellular network itself. Managed Private 5G typically refers to a service offering where a third party (like a mobile carrier or a specialized managed service provider) builds, operates, and manages the private network on behalf of the enterprise, turning it into a turnkey solution.
A2: No. While it is a complex technology, the rise of "network-in-a-box" solutions and managed service offerings is making private 5G much more accessible for industrial enterprises. You no longer need your own team of telecom experts to deploy one.
A3: Yes. Any device with a standard Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or serial port can be connected via an industrial 5G gateway or router. The gateway acts as the device's on-ramp to the private 5G network, translating its native communication to cellular.