Remote Control: Using AT over Telnet for Your Industrial Router
|
|
Time to read 3 min
|
|
Time to read 3 min
The AT over Telnet feature provides a secure and powerful way to remotely access and control a cellular module within an industrial router.
By mapping the AT command interface to an IP network, you can send commands to the device from anywhere in the world.
This functionality is essential for implementing automated remote tasks, such as sending SMS alerts from an unattended device when a critical event is detected.

In the world of industrial IoT, devices are often deployed in remote, unmanned locations like power substations, water treatment plants, or on top of a wind turbine. In my experience, these are the places where on-site maintenance isn't just expensive; it’s often impossible at a moment's notice. So, what happens when a critical event occurs? How do you get an immediate alert without a costly on-site visit?
This is where the power of AT over Telnet comes in. It’s a feature that allows you to manage a router's cellular module remotely. You can do this by using a Telnet client to connect to the router's AT port and send commands as if you were sitting right in front of it. This capability is a game-changer for machine-to-machine (M2M) communication and remote troubleshooting in the field.
At its core, AT over Telnet is a simple yet effective concept. It takes the AT command interface, a standard for controlling modems, and makes it accessible over an IP network. This allows an external user or a script to send AT commands to a device, such as a Robustel R1520 router, via a Telnet connection.

Here’s a quick breakdown of how it works:
This powerful feature allows for seamless remote control, making it possible to manage and diagnose devices without ever being on-site.
Let's walk through a common scenario where this feature is invaluable. I've seen clients use this to set up automated alerts for critical events.
Imagine you have a water pump in a remote area. The pump has a sensor that monitors water pressure, which is connected to your industrial router. You need to be notified instantly if the pressure exceeds a dangerous threshold.

This entire process happens automatically, turning what could have been a costly and dangerous situation into a manageable, remote event.
AT commands are a standard set of instructions used to control a modem . They are used to perform various actions, such as initiating a data call, sending an SMS, or configuring modem settings.
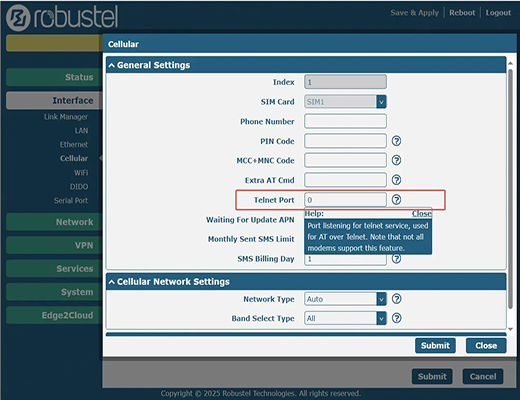
All RobustOS devices, such as the R1520, provide a remote Telnet feature that allows you to control the wireless module using AT commands .
You can enable AT over Telnet access from the router's web interface . You will need to browse to the "Network > Firewall > Filtering" section and turn on "Enable Remote Telnet Access" to allow a remote connection .